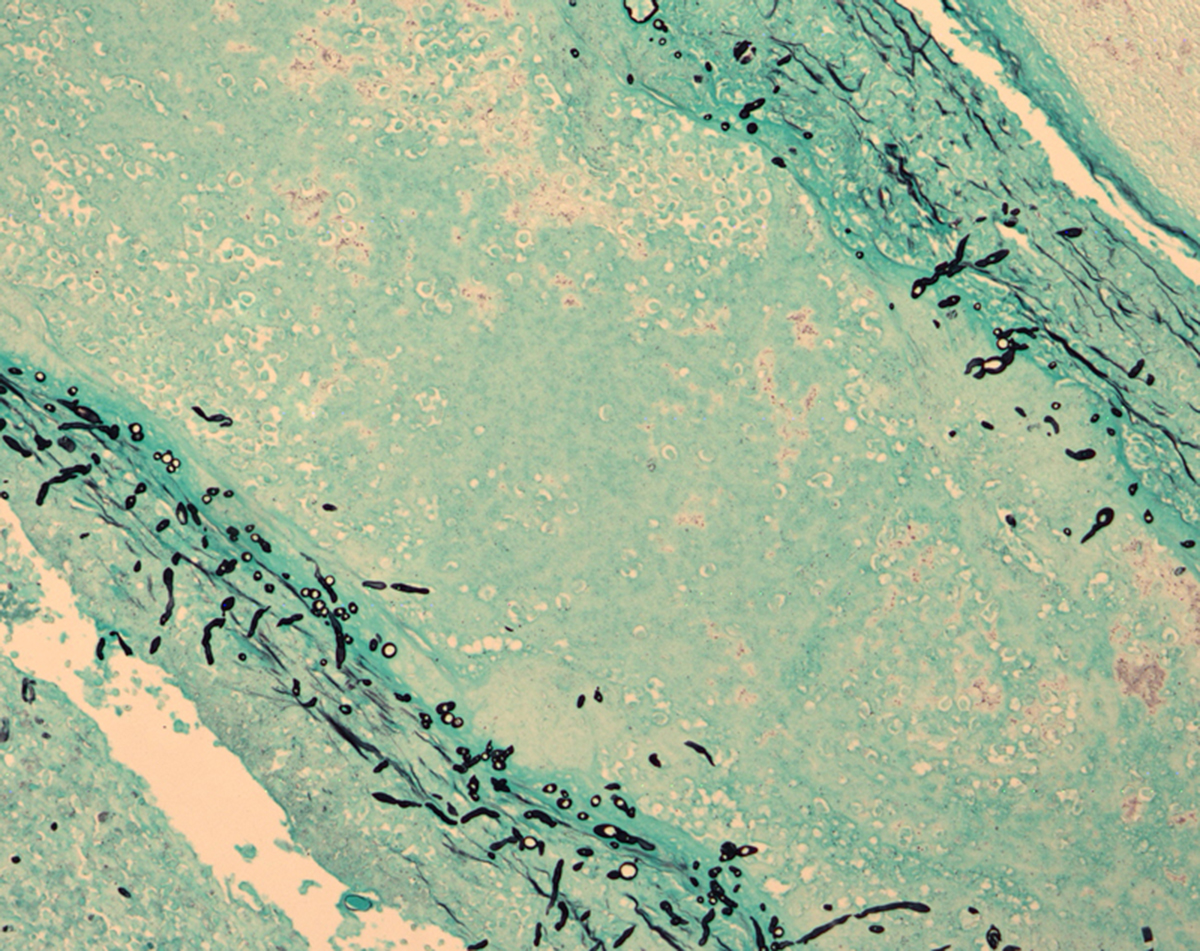
Meningitis is an inflammation of the protective membranes wrapping the brain and spinal cord. This severe and life-threatening disease if not treated, may lead to brain swelling and cause lasting disability, a coma or death.Course of the illness
Meninges or protective membranes around the brain, normally serve to protect the brain from the body’s immune system. In meningitis, this may cause a major problem. If bacteria or virus finds their way to the brain, they also become isolated from the effects of immune system and they can multiply unobstructed. However, if the immune system starts to react and fight the infection, problem may become more severe. When the immune system reacts, blood vessels become leaky and allow white blood cells and other infection-fighting fluids, to enter the mengines and reach the brain. This may result in swelling of the brain and decrease blood circulation to some of the brain areas.
Causes of meningitisCauses of meningitis are numerous. Bacteria may cause the most serious infections. Other common causes of meningitis are virus, fungi and reactions to certain medications or environmental toxins.
Bacterial meningitis occurs in about 3,000-5,000 people in the United States every year, and it is most commonly caused by Streptococcus pneumoniae. Crowded college dormitories or military barracks may be the suitable environment for Neisseria meningitidis bacteria, which also causes meningitis. Haemophilus influenzae type B (Hib) is another bacterial cause of meningitis, but it is becoming less frequent because children now get the Hib vaccine in infancy. Bacterial meningitis progresses rapidly and it is fatal in approximately 20-25% of cases.
Viral meningitis frequently remains undiagnosed and is confused with the flu. However, prognosis for viral meningitis is far better than for bacterial meningitis. Most of the patients completely recover with a simple treatment that does not include antibiotics. Antibiotics are being used only for bacterial infections.
Meningitis may often spread from another infection near the brain, ears or sinuses for example, or may occur as a complication of brain, head or neck surgery.Risk factorsMeningitis affects both men and women in the average age of 25 years. It is not clear why, but African Americans are at a higher risk of developing meningitis than people of other races.
The following groups of the population are at higher risk for meningitis: adults older than 60 years , children younger than 5 years, alcoholics, patients with sickle cell anemia, patients with cancer (especially if they receive chemotherapy), patients who have received transplants and are taking drugs that suppress the immune system, patients with diabetes, people recently exposed to meningitis at home, people living in close quarters (barracks, dormitories), IV drug users, people with shunts for hydrocephalus.













Your thoughts on this
Loading...