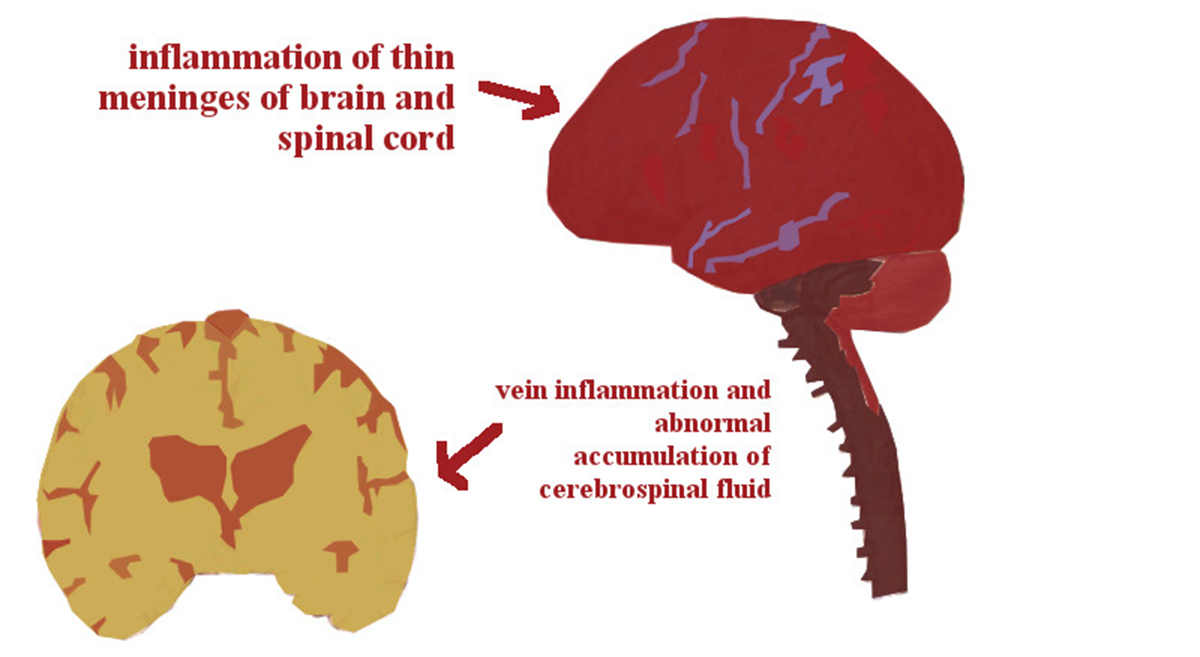
The meninges are the protective membranes surrounding the brain and spinal cord. When they are infected, the condition is called meningitis.
The infection is often caused by bacteria or a virus and when the meninges get swollen they can case damage to the nerves and brain.
Bacterial meningitis is very serious and it should be considered a medical emergency, because if the bacterial infection is left untreated, it can cause severe brain damage and infect the blood as well.
The bacterial form of meningitis is most common in children under the age of five and especially in babies who are not even one year old. It is also common in teenagers.
If the meningitis is viral, it is less serious. This is the most common kind. They are often so mild that, many times, cases of viral meningitis are mistaken as the flu.
Viral meningitis will usually get better with a couple weeks with rest and painkillers.
However, the bacterial kind needs to be treated with antibiotics. Severe cases will involve hospital treatment in the intensive care unit so that the body’s vital functions are maintained.
Bacterial meningitis can place tremendous strain on both the body and brain and it is estimated that a quarter of people who have meningococcal disease (the combination of meningitis and blood poisoning) will see complications. Some of these include hearing loss, problems with concentration and memory, coordination and balance problems, learning difficulties, and epilepsy.
There can also be cases of cerebral palsy, speech problems, or vision loss.
Hearing loss is the complication that most often arises from meningitis, which is why when people are recovering from the condition, they are usually given hearing tests. Even after the meningitis has been cured, the person should take another ear exam in six months to see if the hearing is deteriorating or improving.
If the bacteria enter the blood, poisons and toxins will be produced, which kill healthy tissue. In the most severe conditions, the tissue can become gangrenous, which means that it will probably have to be amputated. This usually occurs in extremities such as the fingers, toes, or a whole limb even, such as the leg or hand.
Particularly for children, meningitis can be a very traumatic experience, and in some cases it can lead to psychological and emotional behavioral changes in which the child can become clingy and need to be close to the parent at all times.
The child can also experience bed-wetting, disturbed sleep, nightmares, aggression, temper tantrums, or fears of doctors and hospitals as a result of the trauma incurred by the meningitis.













Your thoughts on this
Loading...