The meninges are membranes i.e. sheath that covers the brain and the spine cord. As any other tissue inside the body the meninges may get inflamed and this inflammation is medically known as meningitis. There are different infective agents capable of causing meningitis. According to microorganism responsible for inflammation there are bacterial, viral, fungal and parasitic meningitis.
More about Bacterial Meningitis
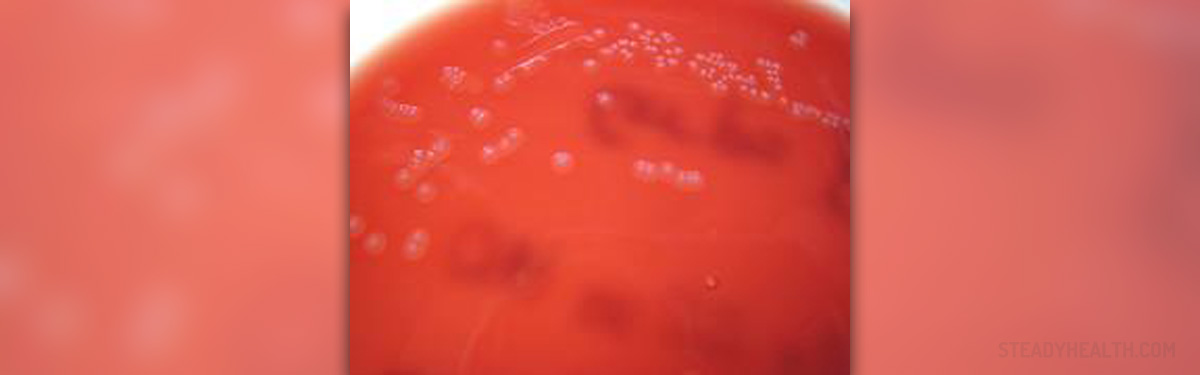
Bacterial meningitis is much more serious than the other types of this disease. It can cause numerous temporary and permanent complications and is sometimes even life-threatening. The most common culprits of bacterial meningitis are Streptococcus pneumonia, Neisseria meningitidis and Haemophilus influenzae. The condition affects people of all ages. However, susceptibility to the infection is a bit higher in infants and children.
Bacterial Meningitis Clinical Characteristics
This bacterial infection is characterized by high fever, headache and stiffness of the neck. Neck stiffness is rather severe. The person simply cannot bend the neck or touch the chest with his/her chin.
Additional symptoms and signs include nausea and vomiting, drowsiness, joint and/or muscle pain, sometimes seizures and photophobia (increased sensitivity to light). Babies refuse to eat, their fontanel is swollen and there may be whimpering cry.
How Long does Incubation Period Last?
Incubation period is the time that passes between exposure to an infective agent and the onset of the very infection (the first symptoms and signs of the disease). In majority of cases this period is between 2 and 10 days. Sometimes, however, bacterial meningitis develops rapidly with first symptoms occurring only a few hours after exposure to the particular microorganism.
It is essential to mention that bacterial meningitis represents highly contagious illness. It is easily transmitted via close contact with an infected individual. The bacteria spread through saliva and nose discharges of the infected person.
Treatment for Bacterial Meningitis
Bacterial meningitis requires prompt and rather aggressive treatment. Only this way potential complications can be prevented and a patient's life saved.
The treatment starts as soon as the diagnosis is confirmed. In order to achieve final confirmation doctors take samples of the spinal fluid (the procedure called lumbar punction). The very presence of bacteria is an indicator of bacterial infection. Patients also undergo additional tests such as blood and urinalysis.
Patients receive potent antibiotics which are supposed to be administered intravenously. Apart from antibiotics depending on the symptoms and signs patients also receive symptomatic treatment. For instance, patients who have developed seizures require anti-epileptic drugs, those with high fever need to receive antipyretics etc. Left untreated the infection may progress and one may end up with a variety of neurological sequelae or even die.
Fortunately, it is possible to prevent some types of bacterial meningitis thanks to vaccination.






-Arthritis_f_280x120.jpg)








Your thoughts on this
Loading...