Bacterial Meningitis - Overview
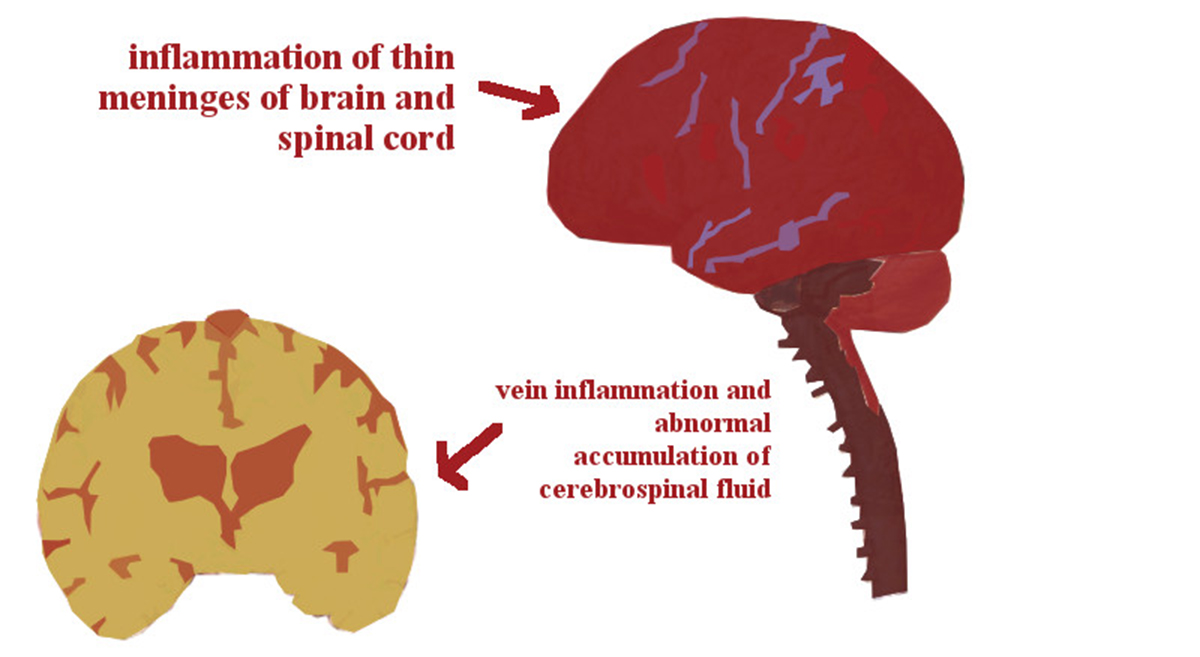
Bacterial meningitis is an inflammation of meninges, membrane which surrounds the brain, caused by bacteria. Apart from bacteria meningitis can be also caused by viruses. There are several bacteria that can cause bacterial meningitis. The disease is rather serious and requires hospitalization and proper treatment since if untreated on time and adequately it may lead to severe complications such as encephalitis, hearing loss and mental retardation. Bacterial meningitis may or may not be contagious which basically depend on the bacteria that causes the infection and measures of prevention that are applied in order to stop the spread of the disease.
Three types of bacteria are responsible for meningitis, Hemophilus influenzae type b, streptococcus pneumoniae and Neisseria meningitidis. Bacterial meningitis cause by Hemophilus influenzae has been almost eradicated due to regular vaccination. This is not the case with other two types of bacteria.
Presentation of Bacterial Meningitis
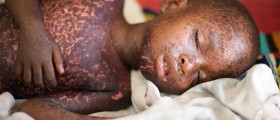
If a person is older than 2 the typical symptoms of bacterial meningitis include increased body temperature, severe headache, sensitivity to light and stiff neck. The symptoms may develop over several hours or in a period of one or two days. Additional symptoms include nausea and vomiting, confusion and sleepiness. In some cases bruises may occur and affect larger portions of the skin.
In infants, the symptoms of meningitis include fever. Symptoms such as headache and stiff neck may accompany the disease, but the babies do not talk so they cannot report headache and sometimes stiff neck cannot be found during physical examination. Babies are typically nervous, they cry a lot, vomit and lose their appetite.
In advanced stages of the disease seizures may occur and they can affect each and every patient.
Is Bacterial Meningitis Contagious
Infective agents in bacterial meningitis are spread by direct contact with infective discharge from the nose or throat. Luckily, the disease is not so contagious and it cannot be spread through air or by a casual contact with the infected person.
All in all, physical contact of any kind with the infected person is strictly forbidden. This is applied until the patients completely recover. All the family members and friends who remain in contact with the infected person require prophylactic administration of antibiotics.











Your thoughts on this
Loading...