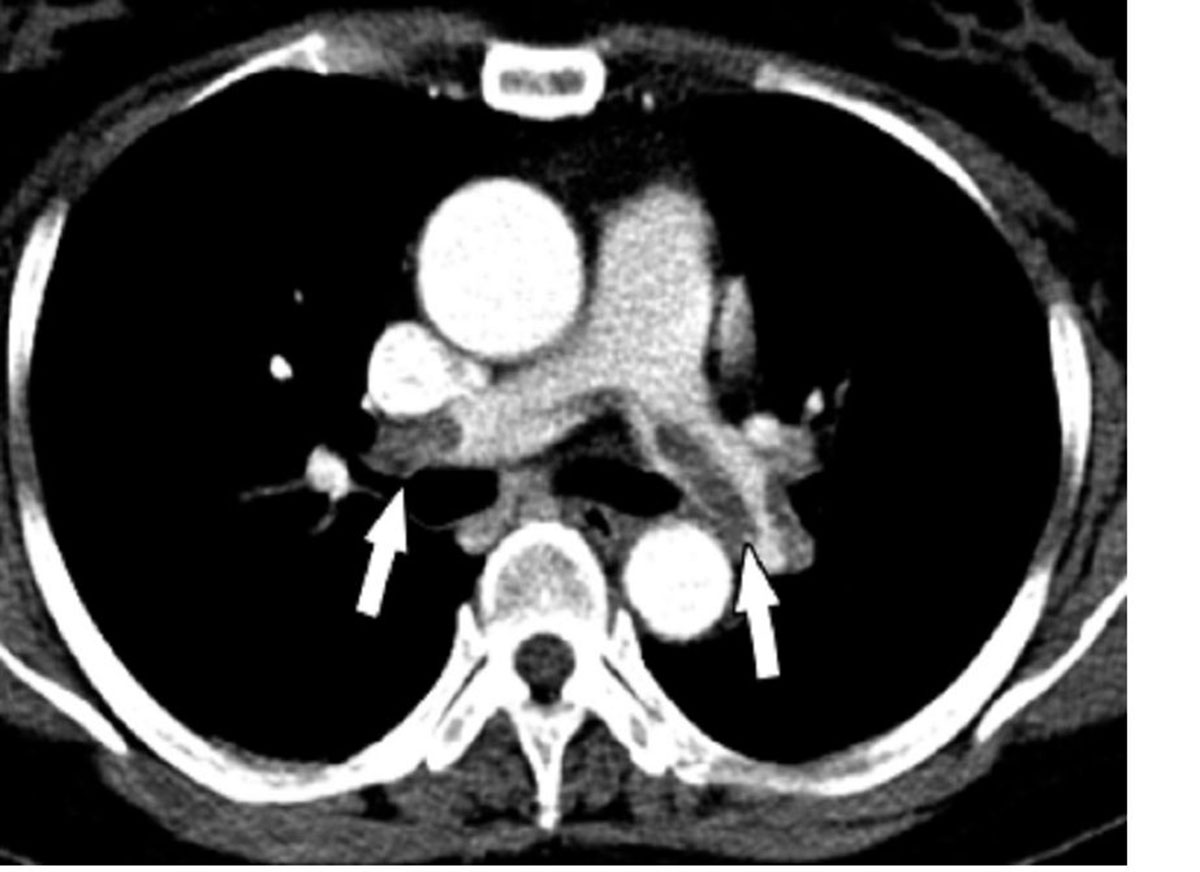
Pulmonary embolism and the main symptoms
Pulmonary embolism is a condition that refers to the blocked artery or more arteries in the lungs. It is one of the most frequent causes of the pain in the chest and shortness of breath, and it can be life-threatening, particularly in situations when this symptom is ignored, which is why it is important to seek for medical help as soon as possible. It can occur even in the people who are healthy, although older people with valve malfunction, some other heart disease, or cancer, are a bit more likely to experience pulmonary embolism. On the other side, people who smoke, are obese, are about to have surgery, pregnant women, and those who take supplements of estrogen are also at higher risk of developing blood clots.
A part of the risk group refers to those in whose families pulmonary embolism runs, as well as those who have to lie in bed, either in hospital or at home, because of some disease or surgery that they have had. Besides the major symptoms, cough can also indicate this condition, as well as wheezing, swelling of legs, increased sweating, irregular heartbeat, and weak pulse.
What are the main causes of pulmonary embolism?
When it comes to the causes of blocked arteries in the lungs, blood clots are the main culprits in the greatest majority of the cases. They generally tend to occur in the deep veins of legs, though not exclusively. However, fat from the marrow of the bone that is broken may also cause the blockage of the artery, as well as it can be blocked by a part of the tumor, amniotic fluid embolus in pregnancy, or air bubbles.
Yet another cause for this condition can also be some kind of a trauma to lower leg, or deep vein thrombosis, which results in the damaged wall of the vessel. Since this blockage results in insufficient amounts of oxygen and nutrients which are carried by blood to the lungs, it means that they are not provided with enough of it, and it will certainly affect the rest of the body.
Complications may be very serious and even fatal if the condition is not treated immediately, but it can also lead to pulmonary hypertension, and the damage of the heart, or at least a part of the heart.
















Your thoughts on this
Loading...