Causes of prostate cancer
Prostate cancer is one of more frequent cancers in men. It usually occurs in 6th and 7th decade of life, and when it comes to people under age of 50, 1% of that population is affected. Unfortunately, main cause of this cancer is still unknown, though possible etiological inducers are genetic predisposition, environment and influence of hormones.
Environmental factors influence the manifestation and symptoms of the cancer. There is no proven fact, but some say that saturated fat and nicotine can be included in etiological factors. Even sexual activity is mentioned as a possible cause. This tells us that prostate cancer shows many variations in patients. As for hormonal causes, androgen hormones react as promotors of the cancer growth and about 80% of the prostate cancers show androgen dependency, which means that, for the multiplication of the prostate cancer cells, presence of androgen hormones is needed. Testosterone greatly improves the development of the prostate cancer cells but it is not the cause of it. Still, its role is used to create several variations of therapy, all including reduction of the secretion of this hormone. It is also proven that risk of prostate cancer appearing is higher, if there are family members that suffered from this malign tumor.
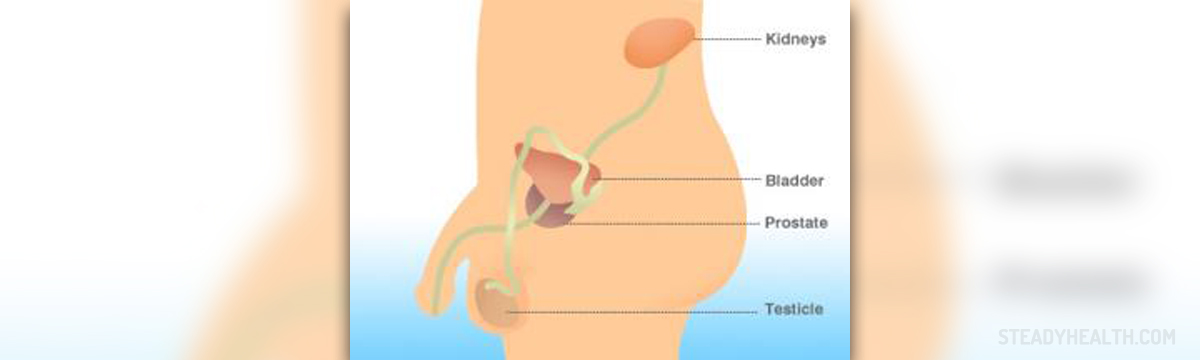
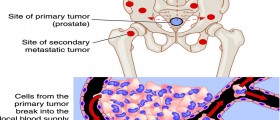
Prostate cancer usually develops in peripheral prostate zone, rarely in the central area and it is usually in adenoma form (95%). This cancer can grow in prostate and then it is called intra prostatic cancer, or it can affect surrounding tissue, when it is referred to as extra prostatic. Spread of the prostatic cancer can be local and peripheral (when cancer cells travel with blood and lymph).
Main symptoms and the treatment
Symptoms and signs depend on the stage of the cancer development. Most common are nocturia, dysuria and polakuria with complete emptying of the bladder, which is typical of the first stage. The second stage begins with incomplete emptying and urine that did not pass through completely, and this phase can last for a couple of years. The third stage starts with complete retention and bladder distension. Patient urinates often, with very small amount of urine, which leads to chronic uremia and liver and kidney dysfunction. Prostate cancer can be diagnosed easily, with a simple rectal examination, and if additional examination is required, transrectal ultrasonography is done.
The treatment includes radical surgery and radiotherapy. Surgery can be done in three ways, including the one with robotic system. Also, so-called pharmacological castration is applied. Less known, but also used is cryotherapy, and if needed, combination of several methods.













Your thoughts on this
Loading...