
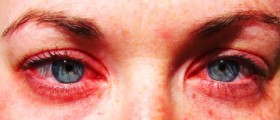
Hayfever is a type of allergic rhinitis with symptoms of sneezing, runny nose, itchy eyes, congestion and sinus pressure. It is a condition where an allergen, such as pollen, causes inflammation inside the nose. It usually occurs in spring and summer, but it depends on which pollens or spores a person is sensitive to. However, hayfever may occur as a result of irritation caused by dust mites.
For many of patients, symptoms are mild and they don't feel a need to seek medical help. Some may suffer so much that they become unable to carry out normal life activities and treatment is the only option.
Allergies are an autoimmune response where the immune system overreacts on a harmless substance taking it as a harmful one. This triggers the reaction and causes the unpleasant symptoms. What actually happens is that the body produces as an antibody - immunoglobulin E - to attack the "harmful body".
Triggers
Some of the hayfever triggers are:
Three pollen - in the spring Grass pollen - in the late spring and during the summer Weed pollen - during the fall Fungi and mold spores - most common in warm weatherIf the person has a family member suffering from hayfever, chances of developing it are somewhat higher. Asthma is another significant trigger for hayfever, as well as sensitivity to some other allergens. Gender and age may also play an important role in triggering hayfever - it affects more young males, especially before the period of adolescence.
After this period, slightly more girls suffer from hayfever and most young males outgrow it. It might be interesting to note that people born during the high pollen season have more chances of developing this condition, especially if they are firstborns or have no siblings and if they are being exposed to second-hand smoke during the first years of life. The unusual statistics also show that babies born in high income families may develop hayfever later in life. An explanation may lie in childhood infections - if a baby has had a small number of infections the risk of autoimmune problems may become more significant.
A treatment of immunotheraphy is often used to gradually increase a person’s exposure to the allergen, modifying the natural course of the disease and thus suppressing and reducing an immune response.



_f_280x120.jpg)











Your thoughts on this
Loading...