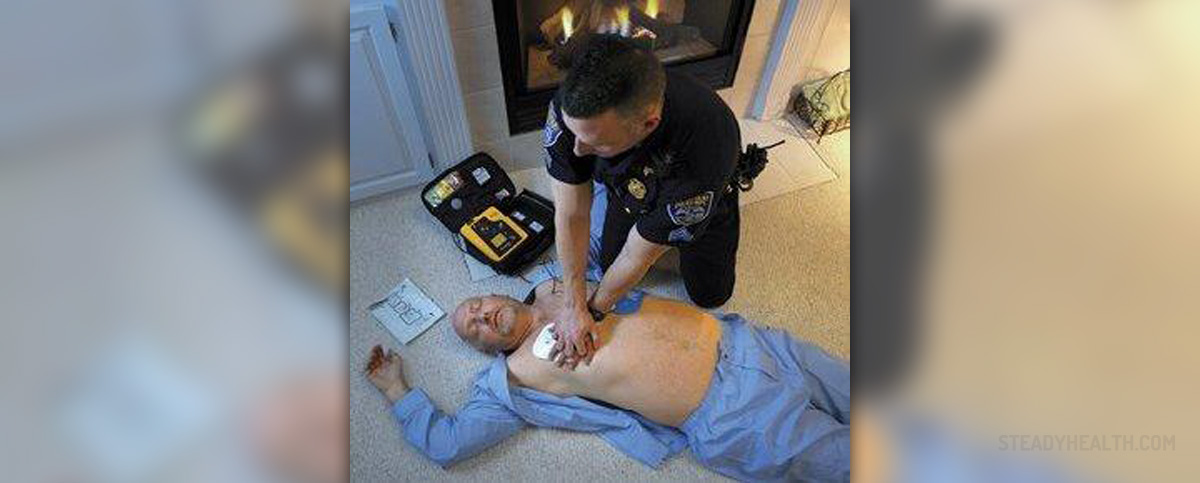
How to recognize the symptoms that might lead to cardiac arrest?
Cardiac arrest is a medical term for the condition that is characterized by a sudden loss of the functions of the heart. The breathing stops and the person loses consciousness, all of which indicates that the situation is very serious and life threatening. Emergency medical help is needed at once.. However, cardiac arrest is not the same as a heart attack because the reason for cardiac arrest is usually electrical disturbance in the heart, which results in stopping the flow of the blood to other parts of the body, while a heart attack occurs when there is a blockage of blood flow to a part of the heart.
Cardiac arrest is practically the same as clinical death. The fact is that it generally occurs without any warning, but sometimes there are some symptoms that might be present like, extreme over tiredness, blackouts, dizziness, pain in the chest, palpitations, and even vomiting and shortness of breath. This is why it is important to see a doctor if any of the signs is frequent.
Although, cardiac arrest can be recognized by the above symptoms, the truth is that these symptoms might indicate some other condition as well, such as syncope, for example. Even if the person cannot identify the condition, it is important to call 911 as soon as possible.
What to do?
Generally, this condition very often has fatal outcome, and it is important to know that only with fast and adequate medical care does the person have a chance to survive. What might improve the chances of the person in question is administering CPR or even rapid compressions to the chest. Regarding rapid compressions, it is important to know that rescue breaths should follow every 30 compressions. In a number of cases, these actions actually helped the person survive until emergency arrived. In case the person wakes up and regains consciousness on their own, then it is more than obvious that cardiac arrest did not happen.
Who is at risk?
The group of people who are at risk of experiencing cardiac arrest includes:
those who smoke or have more than two drinks a day, those who have high blood pressure or high levels of blood cholesterol, those who are obese and suffer from diabetes, as well as those who already suffer from some heart related conditions or have a family history of heart disease or cardiac arrest.













Your thoughts on this
Loading...