Cardiac arrest occurs in situations when the circulation of blood stops being normal due to the failure of the heart to contract effectively. Cardiac arrest is known under other names as well such as cardiopulmonary arrest and circulatory arrest. It is not uncommon for the doctors and other medical staff to refer to this condition as unexpected cardiac arrest or sudden cardiac arrest or simply SCA. Heart attack is not the same thing as a cardiac arrest and people should not mix these two conditions. However, it is not uncommon for the cardiac arrest to be actually caused by a heart attack. Cardiac arrest occurs when not enough oxygen is being pumped by the heart. A lack of oxygen in the brain leads to loss of consciousness and that is followed by abnormal or absent breathing. An emergency treatment within the first few minutes is essential in order for brain injury and even death to be prevented. However, it is easily reversed and treated if the emergency treatment is applied instantly. CPR and defibrillators are considered to be the emergency treatment.
Leading causes of sudden cardiac arrest
There are lots of causes which lead to sudden cardiac arrest but in almost all cases that cause is coronary heart disease. Apart from it, there are even some non-cardiac conditions which are known to drastically increase the risk of sudden cardiac arrest. According to the data, coronary heart disease is the cause of sudden cardiac arrest in almost 70% of all cases. When adults are considered, ischemic heart disease is the leading cause of the actual arrest. In these situations more than one third of all people show signs of recent myocardial infarction at autopsy. Apart from coronary heart disease, there are other cardiac abnormalities which contribute to the increase of risk of sudden cardiac arrest like cardiomyopathy, cardiac rhythm disturbances, hypertensive heart disease and congestive heart failure. Non-cardiac causes exist as well. The experts claim that sudden cardiac arrest is not related to heart problems in approximately 35% of cases. Some of the most commonly seen non-cardiac causes include trauma, non-trauma related bleeding like gastrointestinal bleeding, aortic rupture and intracranial hemorrhage, overdose, drowning and pulmonary embolism. Coronary heart disease and sudden cardiac arrest share a lot of risk factors such as smoking, lack of physical exercise, obesity, diabetes and family history. Certain risk factors cannot be influenced while other can.
Management of sudden cardiac arrest
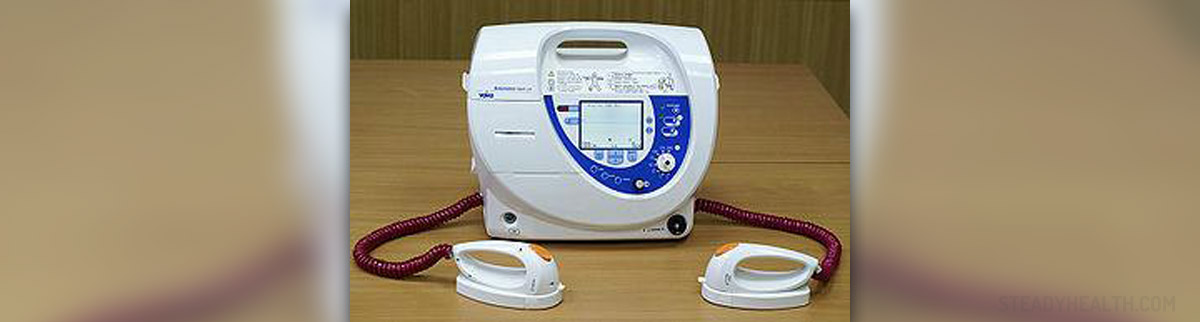
In almost all cases of sudden cardiac arrest the doctors treat it with resuscitation. Cardiopulmonary resuscitation is otherwise known as CPR. This is an essential part of the management of sudden cardiac arrest. It is important that this management begins as soon as the person has suffered from a sudden cardiac arrest. It is also important that there are no interruptions during this management. The doctors claim that the chest compressions are probably the most important part of cardiopulmonary resuscitation. Apart from the chest compressions, tracheal intubation is also important and it proved to increase the survival rates in cases of sudden cardiac arrest. The doctors have divided the cases of cardiac arrest to shockable and non-shockable. This division is based upon the presence or absence of ventricular fibrillation or pulseless ventricular tachycardia. In case of shockable rhythms the treatment consists of CPR and defibrillation. Since heart attack is the leading cause of cardiac arrest outside of the hospital a person suffering from it is most likely to respond to defibrillation. The use of defibrillators increases the chance of survival drastically.
Prognosis and survival rate of sudden cardiac arrest
According to the doctors, those who suffer a sudden cardiac arrest outside of the hospital have less chance of survival than those who suffer from it inside the hospital. A person with ventricular fibrillation or pulseless ventricular tachycardia has up to 15 times better chances of survival than a person with pulselless electrical activity or asystole. Due to the fact that mortality is pretty high in cases where cardiac arrest occurs outside of the hospital, certain programs were developed which should ensure the increase of survival rate. The experts agree that the cause of the sudden cardiac arrest plays the most important role when survival is considered. In case of hypothermia, the chances of survival are high due to fact that cold defends the vital organs from the effects of tissue hypoxia. If toxins are the cause of the arrest, it is pretty important to identify the toxins and provide the proper antidote. 14.6% of those who received resuscitation by ambulance staff survived at least until they reached the hospital. 59% of these do not survive admission and 50% of that number dies within the first 24 hours. 46% of those who survive the admission survive until discharged from hospital. This means that the overall survival rate of cardiac arrest is 6.8%. Almost 90% of these patients go home with either normal brain function or mild neurological disability, 8.5% suffered moderate impairment and 2% of patients ended up with neurological disability. 70% of those who leave the hospital live at least for another 4 years.













Your thoughts on this
Loading...