Respiratory arrest is an extremely serious medical condition and it can be defined as discontinuation of breathing. Human body is normally supplied with oxygen via process of respiration. Carbon dioxide leaves the alveoli while oxygen enters their capillaries and gets into the blood stream. Proper functioning of the entire respiratory tract is essential for adequate exchange of the previously mentioned gases. In case of respiratory arrest this exchange is obstructed due to cessation or complete absence of breathing.
Respiratory arrest may develop as a consequence of certain obstruction in the airway, decreased respiratory drive or severe weakness of the respiratory muscle. In majority of cases respiratory arrest is associated with cardiac arrest and heart attack. However, it may occur as a consequence of other medical conditions. People with respiratory arrest require prompt treatment and the ventilation is maintained with an artificial respirator.
Causes of Respiratory Arrest
This condition may be a consequence of drug overdose (heroin, morphine, codeine etc). Narcotics, anesthetics and barbiturates are generally capable of causing respiratory arrest. Furthermore, overuse and excessive acute intake of alcohol blocks the brain's neurotransmitters and causes respiratory arrest. Any injury and infection of the central nervous system or the spinal cord as well as bleeding in the brainstem is a potential cause of respiratory arrest. In children respiratory arrest is associated with premature birth and seizures. And finally, the condition may be a consequence of a stroke, irregular heart beats, cyanide and carbon monoxide poisoning.
Symptoms of Respiratory Arrest
Respiratory arrest typically features with abnormal breathing accompanied by noisy sounds such as wheezing, stridor and rhonchi. The person evidently has breathing difficulties and he/ she is struggling to take a breath or does not breath at all. The breathing is obstructed and this consequently leads to low levels of oxygen in blood. Lack of blood causes cyanosis, blue discoloration of the skin and mucous membranes. In severe cases patients lose consciousness. And finally, there is no rising and falling, to be more precise moving of the chest. Being considered as a medical emergency setting of the diagnosis must be prompt and treatment ought to start as soon a possible.
Treatment for Respiratory Arrest
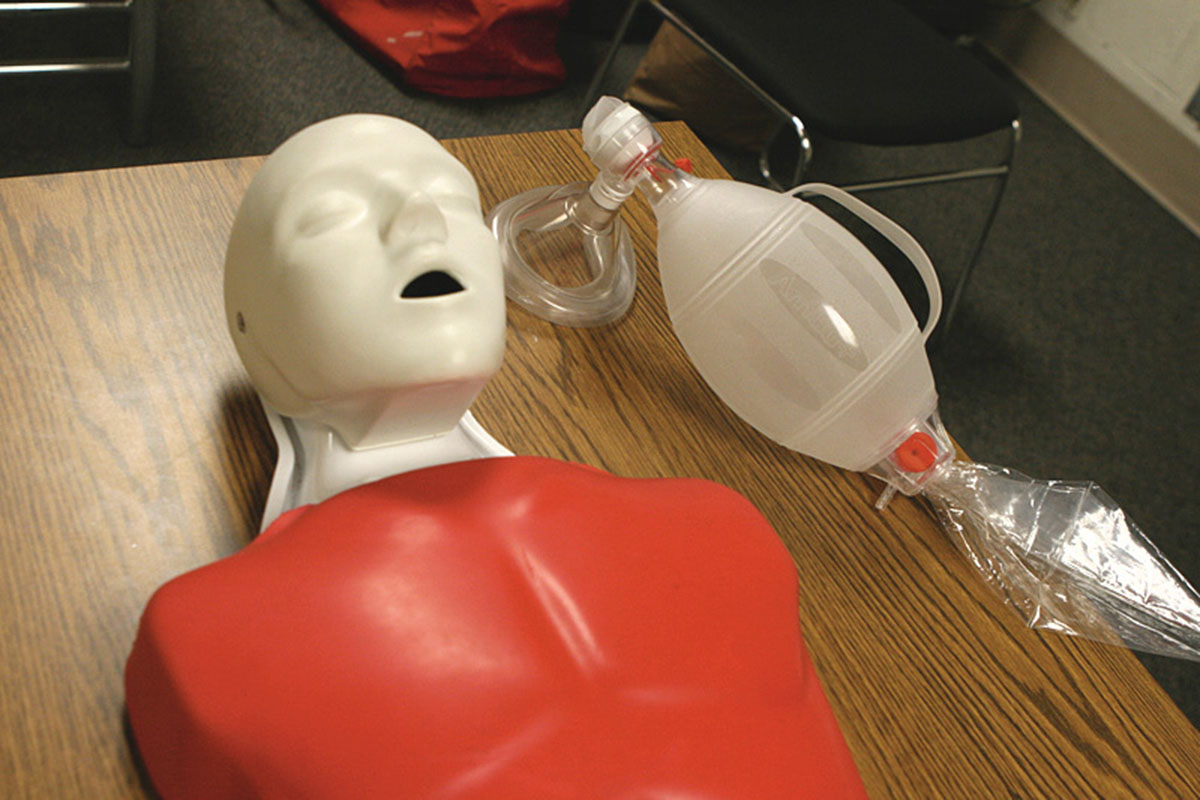
The most serious complications of untreated respiratory arrest are cardiac arrest and irreversible brain damage. Once the symptoms occur it is essential to remove any obstruction in air passage with fingers or forceps (if they are at hand and they are only used by professionals). Infants and small children are placed head down and firmly tapped on the back until the obstruction is cleared. What follows is pulmonary resuscitation i.e. mouth-to-mouth or mouth-to-nose resuscitation. This is only a temporary but highly effective measure in stabilizing the breathing. If there are professionals patients are intubated and their lungs inflated with the assistance of resuscitation bags. Finally, in severe cases patients undergo tracheotomy and are connected to a ventilator.















Your thoughts on this
Loading...