
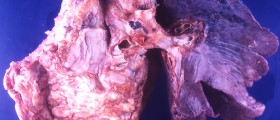
Breast fat necrosis is actually a benign condition which most commonly develops after breast surgery and it may also affect women who have undergone radiation therapy. In some cases breast fat necrosis develops as a consequence of an injury to the breast.
Clinical Characteristics of Breast Fat Necrosis
The lump can be easily felt during a self exam of the breasts. Such exam is supposed to be performed once a month and is highly effective in detection of any growth inside the breasts. The lump may be of different size, shape and may cause asymmetry of the breasts. Furthermore, a woman may notice abnormality of the nipple or discoloration of the skin above the lump (a typical sign of an injury).
Additional symptoms of breast fat necrosis include pain/ tenderness and there may also be a fluid discharge. Dimpling of the skin is possible as well.
Causes of Breast Fat Necrosis
In majority of cases breast fat necrosis is a side effect of surgeries in the breast area (lumpectomy, mastectomy, breast reduction or augmentation, implant removal etc.). It can also occur after radiation therapy. Breast fat necrosis is a common complication of an injury to the breast, particularly in case of blunt chest trauma or a seat belt injury.
Diagnosis and Treatment for Breast Fat Necrosis
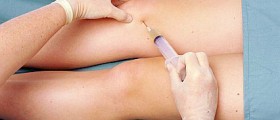
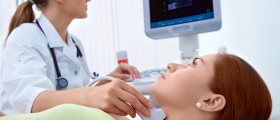
A definitive diagnosis of breast fat necrosis can be set only after certain tests and exams are performed. Namely, a woman first undergoes a breast examination. What follows is mammography or ultrasound of the affected breast. And finally, the doctor performs fine needle aspiration or a core biopsy. Pathological examination of taken samples confirms or rules out the condition.
Breast fat necrosis may withdraw spontaneously. If the lump remains or even gets bigger, a woman undergoes a surgical removal of the affected tissue. Surgery is also performed in case that the condition cannot be confirmed or ruled out even after fine needle aspiration and a core biopsy.
Mild cases of breast fat necrosis require only application of warm compresses and pain killers. Warm compresses are supposed to be applied for about 20 minutes every four hours. Pain is generally alleviated with NSAIDs such as ibuprofen or a salicylate drug Aspirin.







_f_280x120.jpg)


Your thoughts on this
Loading...