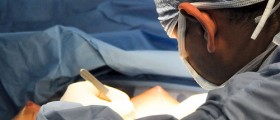
Breast lumps are common in women and may occur due to many causes. A breast lump may form at any age although in post-menopausal and older women it has more chances to be malignant. Diagnosis of breast lumps is made with the help of mammography and breast biopsy. A lump is most often surgically removed except in cases when diagnosis confirms it is benign. Surgical removal of a breast lump is done under general or local anesthesia, as a minor day-case intervention.
Breast Dysplasia
Breast dysplasia is a benign condition characterized by hardening around breast edges in both breasts. Dysplasia refers to altered tissue structure that is usually associated with aging process. It rarely occurs due to serious underlying disease.
Fibroadenosis
Fibroadenosis, also known as chronic mastitis, hyperplastic cystic disease and benign mammary dysplasia, is non cancerous condition that may affect one or both breasts. It is most commonly diagnosed in women aged between 30 and 50. Fibroadenosis may also occur around the menopause or beginning of hormone replacement therapy (HRT) due to hormonal changes.
In younger women fibroadenosis develop due to unknown causes, but experts believe it is also related to hormonal fluctuations since signs and symptoms of fibroadenosis are closely related to menstrual cycles. However, it has been observed that fibroadenosis is less common in women who have breastfed their children.
Symptoms of Fibroadenosis
Fibroadenosis is characterized by lumpiness, irregular breast tissue and presence of cysts. Lumpiness of the breast (nodularity) is particularly noticeable before or during a menstrual period. Breast pain and breast tenderness are also signs of fibroadenosis. Sometimes, fibroadenosis may be accompanied by nipple discharge that may be clear or brownish in color. Also, there may be enlargement of the lymph nodes in the armpits.
Diagnosis and Treatment for Fibroadenosis
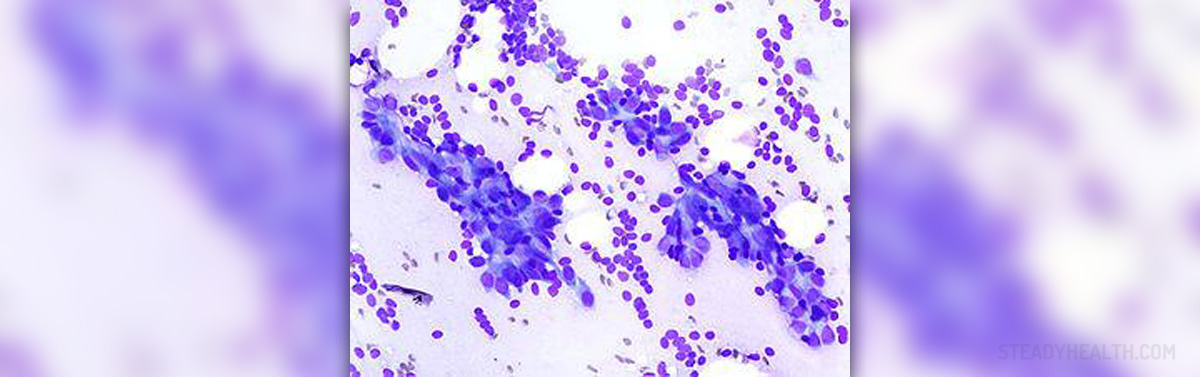
Diagnosis of fibroadenosis involves analysis to determine whether a lump is malignant or benign. Diagnostic tests used for detection of fibroadenosis include mammography and ultrasonography. Fine needle aspiration biopsy is done to rule out malignancy. Biopsies are usually performed in menopausal women as they have increased risk for breast cancer.
Surgical removal of lumps is required only when diagnosis is uncertain. Most commonly fibroadenosis does not have to be treated but the breasts should be re-examined after 2 to 3 months.
Medications like danazol or tamoxifen can be used to reduce breast pain. The pain can be also relieved with Goserelin, hormonal treatment administered via injections. Evening primrose oil can be used for breast massage to relieve breast discomfort.
- medlineplus.gov/breastdiseases.html
- healthfinder.gov/api/Outlink/Search/https/www.cancer.gov/types/skin/moles-fact-sheet?_label_=Find+out+more+about+unusual+moles+and+melanoma+risk
- Photo courtesy of KGH by Wikimedia Commons: commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Breast_fibroadenoma_by_fine_needle_aspiration_(1)_DG_stain.jpg



_f_280x120.jpg)









Your thoughts on this
Loading...