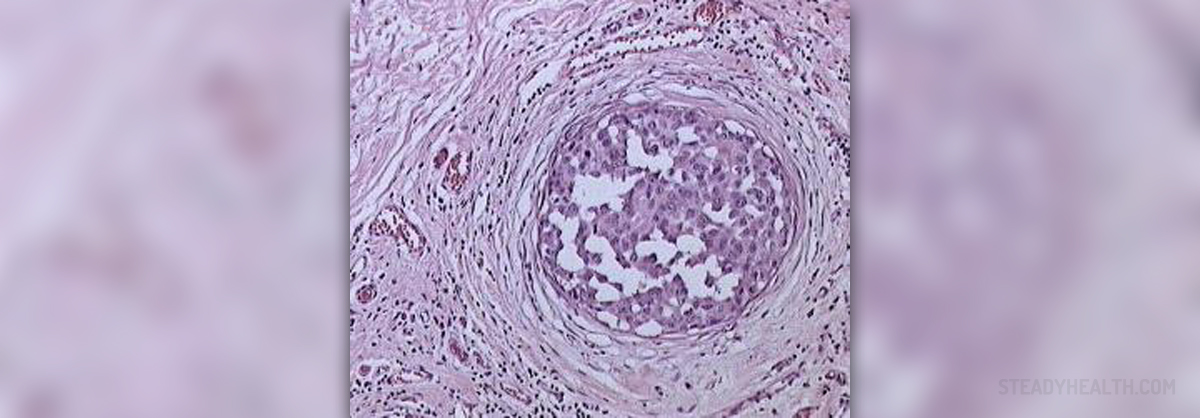
DCIS is short for ductal carcinoma in situ, the earliest form of breast cancer. In this cancer the tumor cells multiply within a milk duct of the breast. DCIS is considered noninvasive and it tends not to spread out of the milk duct to other parts of the breast. The tumor is usually discovered during mammogram screening.
Once the tumor is discovered it needs to be surgically removed and in some cases a woman undergoes additional treatments such as chemotherapy, radiation therapy and hormonal therapy.
Symptoms of DCIS
DCIS is rather small and it may not be palpable. However in a palpable form, a breast lump (if located near the skin) or in some cases, just the very presence of the tumor, can be accompanied by nipple discharge. In a majority of cases women are not aware of the presence of the tumor and it is identified during screening mammogram.
Causes of DCIS
The exact cause of DCIS has not been identified yet, but there are many factors which can contribute to the occurrence of the disease. Namely, certain genes are in charge of tumor suppression. Two genes called BRCA1 and BRCA2 are associated with suppression of breast cancer. A mutated copy of these genes runs in some families and this mutation makes a woman more susceptible to DCIS. Apart from genetics DCIS is also connected to certain environmental factors such as exposure to radiation and specific chemicals. There is even a connection between breast cancer and level of female hormones. And finally, a diet rich in red meat and moderate consumption of alcohol can increase chance for breast cancer.
This cancer also affect older women, who have had a personal history of benign breast disease such as atypical hyperplasia also women with a family history of breast cancer, women who have never been pregnant, women with first pregnancy after the age of 35, women who are taking estrogen-progestin hormone replacement therapy for at least five years or even longer after menopause and women with confirmed genetic mutation of BRCA 1 and BRCA 2 genes.
Diagnosis and Treatment for DCIS
After being discovered by palpation, physical examination of mammography the cancer requires pathohistological conformation. The tissue samples are obtained with core needle biopsy, stereotactic biopsy or surgical biopsy. The tumor is pathologically examined and the diagnosis is either confirmed or ruled out.
The basic treatment modality for DCIS is surgical removal of the tumor. The women suffering from DCIS are treated either with lumpectomy or mastectomy. Pathohistological characteristics of the tumor, its size, number of tumors and additional factors are taken into consideration prior making a decision which surgical approach is most suitable.
After the surgery women may undergo radiation therapy. Once again the doctor decides whether there is a need for radiation therapy after the surgery and the final decision is made after all the characteristics of the tumor are taken into consideration.
And finally, women whose tumor is associated with hormones are administered tamoxifen, the medication that can successfully block the action of estrogen, a hormone that in some women fuels breast cancer and promotes the growth of the tumor.



_f_280x120.jpg)









Your thoughts on this
Loading...