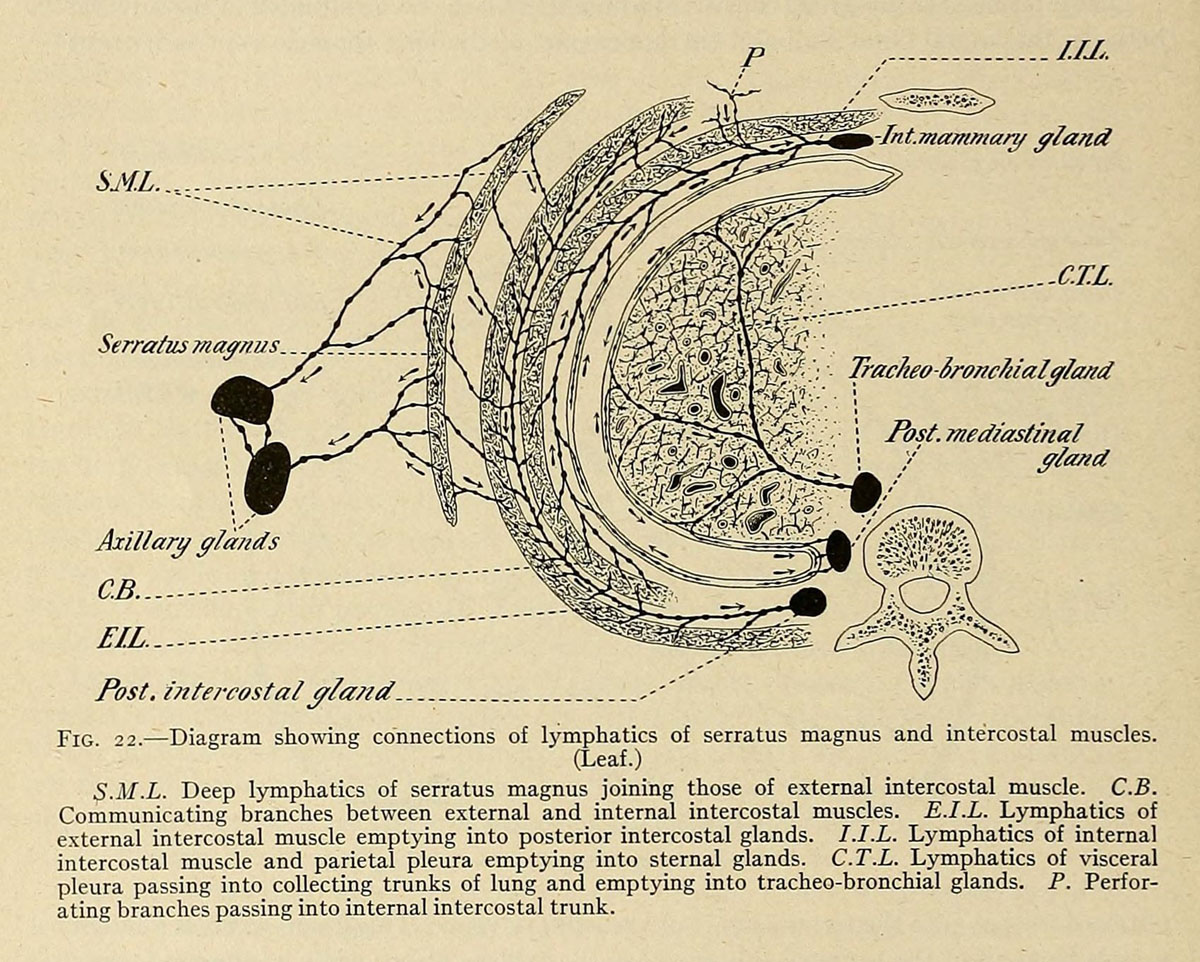
Breast infection is medically known as mastitis and represents an inflammation of breast tissue. It most commonly develops during breastfeeding. The infection typically features with pain, swelling, redness and increased temperature of the affected breast. Breast infection develops as a consequence of bacterial entrance into a milk duct. The bacteria usually originate from baby's mouth and enter the breast through cracks in the nipple. Breast bacterial infection is not so serious, but is definitely very painful. Apart from breast infection that occurs during breastfeeding, mastitis may also occur in some women suffering from breast cancer. That condition is known as inflammatory breast carcinoma.
What Causes Breast Bacterial Infection?
As it has already been mentioned breast infection most commonly affects breastfeeding women. However, even women who are not breastfeeding may develop breast infection even though this occurs in rare cases. Women suffering from diabetes, chronic illness, AIDS and impaired immune system are more susceptible to mastitis comparing to healthy women.
The infection is caused by bacteria normally found in the baby's mouth and they enter the breast ducts via small cracks in the skin of the nipple. The infection is either in a form of superficial small area of inflammation or a deeper walled-off infection (an abscess). It is estimated that around 1-3% of all breastfeeding mothers develop mastitis and the infection most commonly occurs within the first few weeks after delivery. Chronic mastitis affects women who are not breastfeeding. This condition may affect postmenopausal women in whom breast infection develops as a consequence of chronic inflammation of the duct below the nipple. Hormonal changes are responsible for blocking of the milk ducts with dead skin cells and debris and once the duct is clogged the risk of infection significantly increases.
Clinical Characteristics of Breast Bacterial Infection
The affected breast is warm, tender and the skin is red. There is also breast swelling and a woman feels tired. Additional symptoms that occur in more serious inflammation are fever and chills. Abscess is a complication of bacterial breast infection. This is a harmless and a noncancerous mass. It is tender and free mobile beneath the skin. In serious infection there may be pus draining from the nipple, persistent fever and progression of the symptoms.
Bacterial Breast Infection Treatment
At home a woman may take pain relieving medications such as acetaminophen or ibuprofen. They are allowed and safe to take during breastfeeding. Mild cases of mastitis do not require antibiotics. It is essential not to stop breastfeeding even though it may be painful. In case there is remnant milk in the breast it can be eliminated with a breast pump. Additional relief can be obtained from warm compresses that should be applied onto the affected breast prior and after feeding. In moderate forms patients are prescribed antibiotics. Doctor pays attention to which antibiotic he/she will prescribe since a woman is breastfeeding. In case the infection progresses and an abscess forms the woman undergoes surgery. Abscess requires proper draining. The woman is first administered a local anesthetic and the doctor then makes a small incision that allows the abscess to drain. Abscesses located deeper in the breast are treated with surgical drainage performed in the operating room.













Your thoughts on this
Loading...