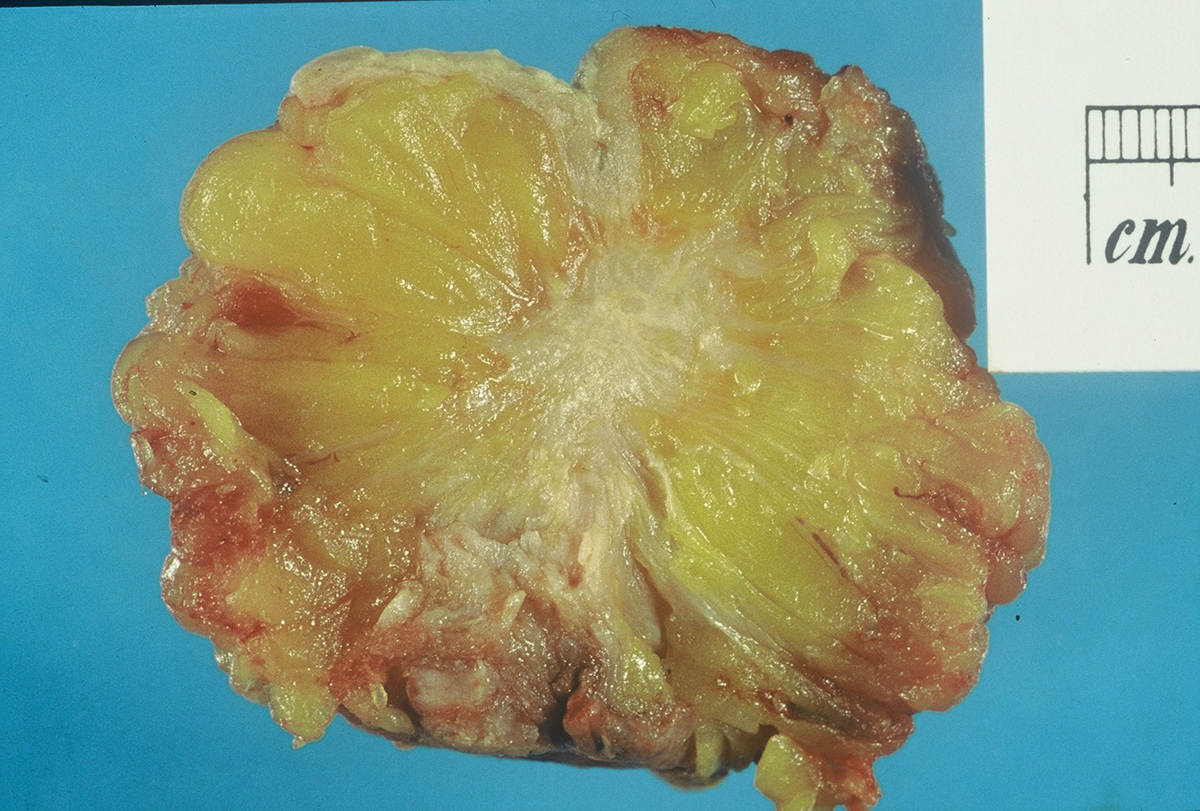
Breast lumps are changes in breast tissue. There are different causes of breast lumps. Some of them develop due to infection, some develop as a consequence of injuries and the last group of breast lumps are breast tumors (non-cancerous growths and breast cancer). In spite the fact that not all breast lumps are malignant a woman should consult her doctor and report any lumps she has felt during self breast exam.
Breast Lumps and Infections
Infection and inflammation of the breast tissues is medically known as mastitis. It generally affects women who breastfeed their babies. Mastitis develops once the bacteria enter through the damaged or cracked skin of the nipple. This can cause hardening of the entire breast or some of its parts. In some cases one or several milk ducts can get clogged and this blockage is actually felt as a breast lump.
Breast Lumps and Injuries
Trauma to the breast tissue leads to a rupture of blood vessels and localized bleeding (hematoma). This localized bleeding may be felt as a lump. In some cases damage to the fat tissue of the breast causes fat necrosis and formation of lumps. These lumps are not harmful and never progress into a malignant disease.
Benign Breast Growths
Benign breast growths include fibroadenomas, breast cysts and fibrocystic breast changes. Fibroadenomas are quite common breast lumps. They affect women during their reproductive years. These are solid and firm tumors, painless or may be tender to touch. Breast cysts are fluid filled sacs that usually occur in women older than 35. The cysts may vary in size and can be a cause of breast tenderness. And finally, fibrocystic changes represent lumpy irregularities in the breast. They develop as a result of an increased sensitivity of breast tissue to hormonal changes.
Breast Cancer
Breast cancer is the most serious breast lump and the only one that can cause lethal outcome. Breast cancer develops as a painless lump and depending on the stage of the disease, location of the tumor and several more factors patients may complain about nipple discharge, inflammation of the skin, breast tenderness and enlargement of the lymph nodes in the armpit.
Evaluation of Breast Lumps
Women (as well as men) who have palpated a breast lump should consult their doctor as soon as possible. The doctor will investigate the patient's medical history, perform physical examination as well as several other tests in order to identify the underlying cause and set the definitive diagnosis. Imaging methods used in evaluation of breast lumps include ultrasound, mammography, MRI and finally some patients undergo biopsy and pathohistological evaluation of the breast lump.














Your thoughts on this
Loading...