
Everybody has at least once experienced groin boil during lifetime. Unfortunately, some people have to face this skin condition more often. This particularly refers to people with weak immune system and those suffering from diabetes and certain skin disorders.
Causes of Boil on Groin
There are several causes of boils on groin. In many people the condition develops due to ingrown hair and it may be also associated with blocked sweat glands, which cause rapid multiplication of the bacteria and formation of the boils. Any break in the skin (small cuts, scrapes etc.) can be a trigger for boil formation. And finally, boils may develop as a consequence of lodging of foreign materials in the skin.
Presentation of Boils on Groin
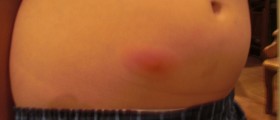
The affected skin is red and tender to touch. The pain may be induced by touching a newly formed bump or it may even occur spontaneously. In a few days the boil becomes larger and fills with pus. Due to pus accumulation the boil appears yellow-whitish in color. This is characteristic for the center of the boil while the surrounding area stays red. In case of multiple groin boils the patients may develop additional symptoms such as fever and swelling of the regional lymph nodes.
Treatment for Boils on Groin
One should seek for medical attention as soon as the boil develops. This medical condition must be treated properly and if left neglected it may cause serious complications. For example, if the pus leaks from the boil it may cause formation of additional boils and in case the infection spreads onto the underlying tissues one may develop abscess. In rather rare and completely untreated cases the bacteria may enter the blood stream and cause life-threatening sepsis.
The patients are prescribed antibiotics according to the antibiogram. Antibiotics are especially important in case of large boils or recurrent boils. Furthermore, all boils must be properly drained. The process of draining can be accelerated by application of a cloth soaked in warm salt water. The healing can be also promoted with antibiotic creams. One should not try to squeeze a boil under no circumstances. If the boil does not drain spontaneously, a doctor will make a small incision and allow the pus to leak out.
















Your thoughts on this
Loading...