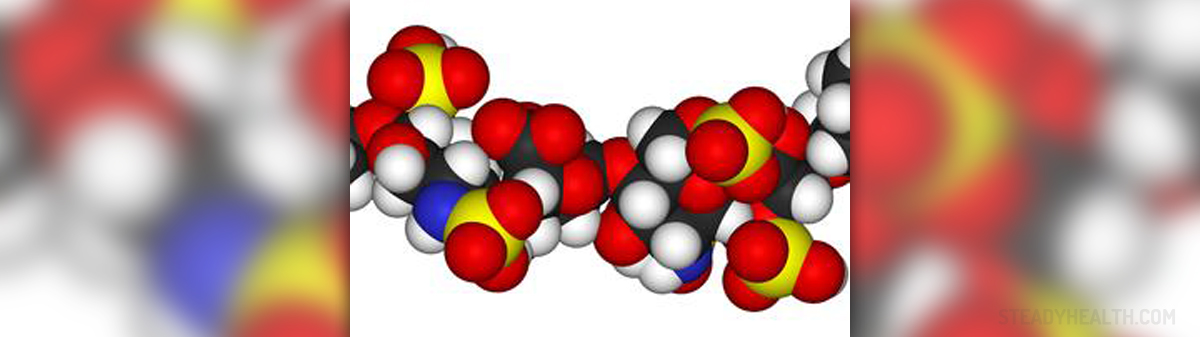
Anticoagulants are specially designed medications which act against coagulation of blood, successfully dissolve blood clots and prevent their formation in the first place.Blood Thinners
Our blood has many different components all of which perform specific function. Blood clotting is a vital mechanism that prevents exsanguination due to loss of blood vessels' integrity. The very process of blood clotting employs platelets and certain factors of coagulation which all contribute to formation of a blood clot. The clot closes the opening in the damaged blood vessels and prevents further loss of blood.
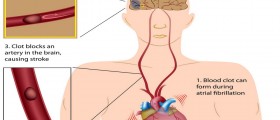
However, some people may have issues with coagulation and become prone to blood clots. In case blood clots are formed uncontrollably and unnecessary, they may easily dislodge, be carried by the bloodstream and eventually clog vital arteries like the ones supplying the heart or the brain with oxygen and other important nutrients. These patients may benefit a low from anticoagulants.
Blood thinners or anticoagulants are drugs that basically interfere with the process of coagulation in different ways. It may not be completely correct to refer to anticoagulants as blood thinning agents since they do not make blood less dense but instead prevent the process of coagulation to certain extent.
The Most Popular Anticoagulants
Currently the two most popular anticoagulants are heparin and warfarin.
Heparin is a biological substance, a very powerful anticoagulant that activates antithrombin III and this way prevents thrombin from clotting blood. The medication is routinely administered intravenously once blood clots are confirmed. Intravenous route of administration allows blood clots to quickly dissolve and jeopardized blood flow to be restored in no time. In case there is no medical emergency heparin is administered either by drip or in the form of subcutaneous injections.
Warfarin is another anticoagulant but unlike heparin that does not come in the form of pills or tablets, warfarin is always administered in these forms. The anticoagulant achieves its effects by interfering with vitamin K, an important participant in blood clotting. Patients who are prescribed warfarin are due to undergo regular check-ups. Their blood and certain components of blood are checked which gives insight in whether the dose is optimal or it needs to be adjusted. What is more, when on therapy with anticoagulants, especially warfarin, patients are supposed to abstain from alcohol and certain types of food which may increase/reduce the effects of the drug. Additional care is essential when patients are taking several more drugs.
Today there are a few more anticoagulants available. Dabigatran and rivaroxaban are two of them. They may achieve a stable level of anticoagulation effects if taken regularly but their dose needs to be adjusted appropriately from time to time.
Finally, there is one more medication that does not actually interfere with the process of coagulation but is efficient against excess accumulation of platelets. Namely, Aspirin inhibits production of thromboxane, the substance that binds platelets together and allows formation of a patch over damaged walls of blood vessels. Now, these patches, once they form, gradually enlarge and may eventually block blood flow. So by taking Aspirin on a regular basis, one may prevent certain health complications associated with uncontrollable platelet accumulation such as heart attacks, strokes etc.How are They Used?
Anticoagulants are routinely prescribed to individuals who are at risk of blood clots as well as those who have already experienced health issues related to blood clots.
For example, patients who have artificial heart valves are at permanent risk of blood clots. They need to take anticoagulants for the rest of their lives.
Furthermore, people who have had a heart attack or stroke are also due to take these medications on a regular basis. By doing so, they will prevent recurrent blockage of certain blood vessels and additional complications as well as lethal outcome they are commonly prone to. Normally, in case of hemorrhagic stroke patients do not receive anticoagulants because these medications may additionally increase bleeding and trigger more complex damage to the brain.
Anticoagulants are also indicated in patients suffering from heart rhythm abnormalities such as atrial fibrillation. Inadequate contraction of heart atria allows blood to clot and such patients easily end with stroke or other health problems if blood clots formed inside the atria do not dissolve.
These medications are also essential for patients who undergo orthopedic surgery and are a standard treatment for individuals suffering from deep vein thrombosis.
Finally, patients with angina as well as those who are supposed to have stent insertion receive anticoagulants routinely.
When it comes to dose adjustment, doctors take into consideration many factors and data obtained by examining patients and performing specific laboratory tests. International normalization ratio (INR) is a test used for determining the speed of blood clotting. Individuals who are not taking anticoagulants have an INR between 0.8 and 1.2 while once the treatment starts this parameter increases. In case INR is way too high a person may be at increased risk of bruising or excessive bleeding and the dose must be reduced. On the other hand, low INR means that the drug is not efficient enough and blood clot cannot completely dissolve. In such case the dose is increased.
- medlineplus.gov/bloodthinners.html
- www.nhs.uk/conditions/anticoagulants/
- Photo courtesy of Benjah-bmm27 by Wikimedia Commons: commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Heparin-3D-vdW.png











Your thoughts on this
Loading...