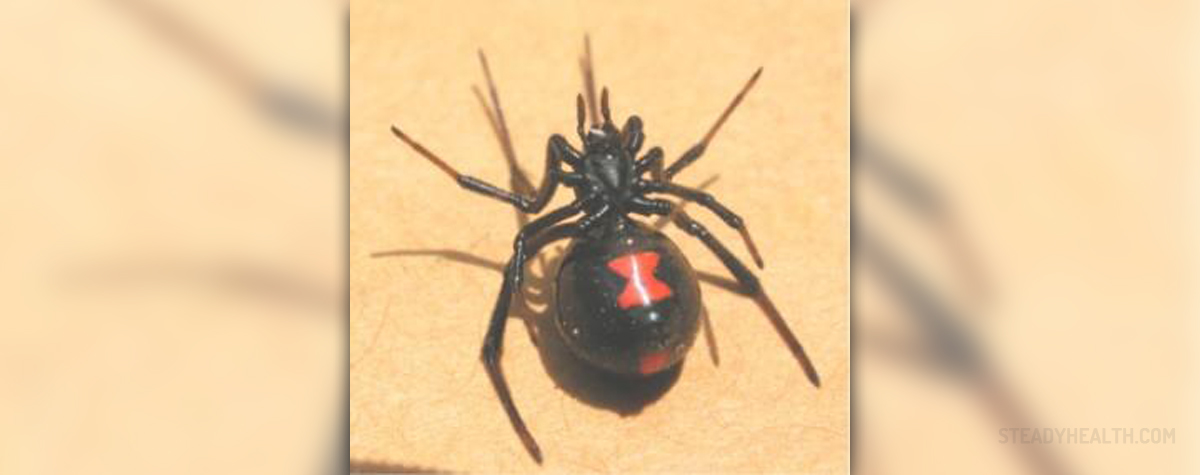

Most people fear the very thought of the highly venomous black widow. This spider got its name due to the distinctive black and red colors on the back and the fact that females of the species often eat the males once the mating process is done.
Description
Latrodectus mactans is the official name of this spider and it belongs to the genus Latrodectus. This type of spider is native to Canada, Mexico and the US. The most notorious of all traits that this spider possesses is its capability of delivering deadly venom upon biting a person.
The reproduction process of this species is quite interesting. Namely, the male spider creates a sperm web which he uses for depositing semen on. Then, once in contact with the female, the male inserts his palpus into the spermathecal openings of hers. Once the fertilization process is complete, the female black widow stores the eggs in a silk-made container. Up to 400 eggs can be stored in a single container and a common black widow spider deposits up to nine sacs of this type during a single breeding season.
Regardless of the number of eggs, only a hundred or so will survive the process. Once properly developed and prepared for breeding, the female black widow spiders are known to live for up to five years. On the other hand, males live much shorter lives, due to the fact that, in a vast majority of cases, the female consumes the male once the reproduction process is complete. Nevertheless, many males manage to escape this fate and these specimen usually move on to fertilizing other females.
These spiders mostly eat other insects or even woodlice, diplopods, chilopods and some other types of arachnids. Once a black widow spider catches its pray inside its net, it quickly moves on it, wraps it in silk and bites it at the end of the ritual, delivering deadly venom. The venom takes it toll over the course of 10 minutes during which the black widow holds its pray securely. Once the victim is dead, this spider releases digestive enzymes into the wound, taking the prey with them in order to feed on it.
The black widow spider has its common enemies too. Mainly, it is in constant conflict with the members of the wasp family, many of which attack both the eggs and the adult black widow spiders.
Venom
Many spiders are much larger than the black widow one. However, this fact does not make the venom this spider delivers less severe. Basically, the black widow spider delivers the venom through their hollow chelicera, resembling needles which are about 1mm long. This length is enough to reach the parts of the skin where serious damage can be done. Yet, males are much smaller and have smaller “needles”, making them less dangerous.
Due to the small amounts of venom that an adult black widow spider delivers, its bite can rarely kill a human being. Regardless, it can trigger quite severe and painful side-effects.
In fact, according to statistical data from various researches carried out in the US, about 63 people died from the black widow spider venom in the period between 1950 and 1959. On a global scale, before the antidote for this spider's venom was developed, about 5% of all bites resulted in death.
If the bite from this spider does not trigger death, it is bound to lead to serious swelling and many other health issues. Sometimes, the spider delivers no venom upon the bite, decreasing the severity of the symptoms significantly. On the other hand, if the venom is injected into a human being, headaches, rashes and itching, sweating, dizziness, tearing of the eyes and excessive salivation, chest pain, hypertension, breathing issues, vomiting and nausea, burning and redness and many other symptoms may appear.
Treatment
If a black widow spider bites you, which is not likely to happen since these spiders have not killed anyone for more than 10 years, do not panic. Rather, stay calm, disinfect the bite wound with soap and warm water. Should you experience muscle cramps, seek medical assistance immediately.
When hospitalized, you will be treated with medications which can deal with the symptoms of the venom.
Before you receive adequate medical help, you can apply ice compress onto the bite spot or apply an antibiotic lotion. Keep the affected part of your body elevated, in order to prevent swelling. Finally, if you can, take the spider that bit you in a plastic bag and show it to the medical staff, even if you have killed it beforehand.
To sum up, these spiders are known to be quite dangerous and the female parts of the species are exceptionally notorious. However, their venom is not delivered in quantities sufficient for killing a human adult in most cases. Regardless, if you get bitten, refrain from panicking, take good care of the bite wound and seek medical assistance immediately.
















Your thoughts on this
Loading...