
Polyps are considered benign tumors which protrude from the mucous membrane. These benign growths can affect many parts of the body. However, they are most commonly found in the uterus, colon, cervix, nasal cavity, sinuses, urinary bladder and stomach.
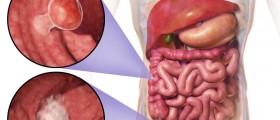
Colon polyps form inside the large intestine. Some of them are benign while others represent precancerous lesions which can at some point develop into an actual colon cancer. This is why all polyps in the colon require resection and pathohystological evaluation.
In many cases colon polyps are asymptomatic. If they cause any symptoms or signs these generally include rectal bleeding, blood in stool, constipation, diarrhea or abdominal pain. Colon polyps are most commonly detected during routine colon cancer screening (colonoscopy).
What are Types of Colon Polyps?
All colon polyps are classified into four types, hyperplastic, adenomatous, inflammatory and malignant.
Hyperplastic colon polyps are tiny and they predominantly form inside the rectum. These polyps are not very potent when it comes to becoming malignant. Definitive conformation of hyperplastic polyp is made after pathohistological examination of the resected tumor.
The most common type of colon polyps are adenomatous polyps. These tumors carry a greater risk for colon cancer. If not removed on time they can eventually transform into malignant form of the disease. There are three subtypes of adenomatous polyps, villous, tubular and tubulovillous.
The third type of colon polyps is a malignant colon polyp. This type of polyp actually contains malignant cells.
And finally, the forth type of colon polyps represent a false polyp. These polyps are known as inflammatory polyps and they develop as a reaction to chronic inflammation of the lining of the colon.
Tubular Adenoma Polyp
Tubular adenoma polyp is one of three subtypes of adenomatous polyps. This tumor has the least potential to transform into colon cancer. Tubular adenoma polyps are most commonly found in the rectum and they are velvety in appearance. They have a tube-like structure. 75% of their epithelium is arranged in a tubular fashion. These growths may be in sessile or pedunculated form. Small tubular adenomas are always considered benign. They are common in adults and in case their size exceeds 2 cm in diameter the risk for colon cancer significantly increases.
Some people are prone to colon polyps. They are due to undergo regular colonoscopy. Only this way the doctor can detect polyps on time and may perform resection. Timely resection is the most effective preventive method for colon cancer. Routine colonoscopy is indicated in all people with hereditary colon cancer, family history of colon polyposis, people with first degree relative with colon cancer or adenomatous polyps, people with personal history of adenomatous polyps and people with personal history of colon cancer.










Your thoughts on this
Loading...