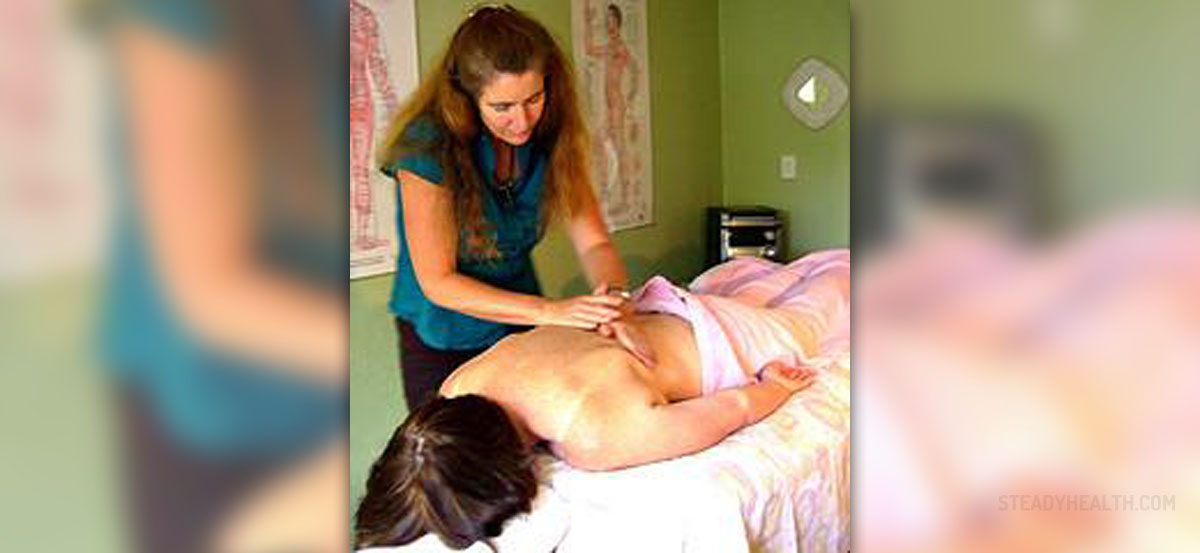
Craniosacral therapy, also referred toas CST is a treatment method commonly used by osteopaths, massagetherapists, naturopaths and chiropractors. During the procedurebehind the CST, the therapist places his/her hands on the patient,tuning into the craniosacral rhythm, focusing on massaging the skull,the spine and the connective tissue in the area, removing anyobstacles present in the nerve passages, promoting the flow of thecerebrospinal fluid and aligning the bones at the same time.
Due to this number of benefits relatedto the CST, it is usually practiced on people who suffer fromconditions such as the TMJ syndrome, neck and backaches, stress,headaches and migraines or some more complex conditions likefibromyalgia.
Gentle Massage of the Bones
Since the CST involves massagingspecific parts of the body gently, its main purpose is relieving thepatient of stress and improving the range of movements of the body.Cancer patients commonly find relief in this procedure.
According to various researchstudies on the subject of CST effectiveness, this form of massagepromotes the flow of cerebral fluids, normalizing, balancing andremoving any obstructions in the craniosacral system, ranging fromthe base of the skull to the base of the lower back.
This procedure was initially developedby Dr. William G. Sutherland in the first years of the 1930s. Theinitial name for this therapy was cranial osteopathy and thetechnique was later improved by John E. Upledger, DO in the 1970s.
The theories behind the craniosacraltherapy do not match the principles of anatomy and physiology of theskull, the brain and the flow of the spinal fluids. Additionally,only a small number of studies was carried out on the subject,especially when it comes to experiments which were in favor of theCST. Therefore, in order to prove the effectiveness behind thismethod, more scientific studies need to take place and show positiveresults. Nevertheless, the number of patient who reportedimprovements of their well-being after this therapy cannot be takenfor granted.
Bear in mind that the CST is notadvised to be practiced on children older than 2, due to the factthat the bones in their skulls are not developed fully at this age.Thus, any form of head massage could lead to bone malformations orsome other health problems. Additionally, people who suffer fromcancer and arthritis should not undergo this therapy withoutconsulting with their doctors first. The movement and manipulation ofthe joints and the tissues may not be beneficial for them and this iswhy they should be cautious.
The therapy usually lasts for about anhour. The therapist first analyzes the base cranial rhythm of thepatient and, then, creates a still point in the rhythm at the base ofthe skull. Once this is done, he/she rocks the sacrum and lengthensthe spine in its lumbar-sacral area, moving on to the pelvicrespiratory and thoracic diaphragms later. Subsequently, thetherapist releases the hyoid bone in the throat and addresses each ofthe cranial bones. Note that the steps may vary and get interchanged,depending on the therapist and the purpose of the CST.
What is Craniosacral Therapy Used for?
Taking into consideration that thisform of therapy is, in fact, a combination of chiropractic andosteopathic medicine, it can help patients suffering from manydifferent forms of diseases. Apart from the main purpose of thistherapy, being the removal of stress and tension, it can also be usedfor treating back pain as well as the pain in the neck area.Additionally, people who suffer from temporomandibular jointproblems, also referred to as TMJ issues can find relief through thecraniosacral therapy.
Furthermore, chronic fatigue,coordination and mobility problems, eye complications, depression,hyperactivity disorders, ADHD, ADD, central nervous system problems,issues related to one's immune system or the endocrine system as wellas a whole plethora of other medical conditions, all can be treatedand dealt with through this method of alternative medicine.
Sometime, CST is used on infants.However, this form of usage is solely restricted to babies who suffered from cartilage and skull membrane injuries sustained duringlabor.
The fingers of the therapist involvedin the CST are medically referred to as the thinking fingers, beingcapable to sense something called the craniosacral pulse and, therebysense the rhythm of this area, knowing what further therapeutic stepsneed to be taken in order to promote healing.
To conclude, craniosacral therapy forthe head focuses on the whole craniosacral area, spreading from thebase of the back to the base of the skull. This therapy involves agentle massaging process, concentrated on bettering the circulationof the craniosacral fluids. Even though there is little scientificevidence in favor of this procedure, many patient claim that theyhave found relief through CST.















Your thoughts on this
Loading...