
Valley fever is a fungal infection caused by Coccidioides immitis or C. posadasii. It is also known as California disease, Desert rheumatism, San Joaquin valley fever and Coccidioidomycosis. This infection is endemic in certain parts of Nevada, California, Arizona, New Mexico, Utah and Texas. These fungi are usually found in soil of listed areas and they are becoming air-borne when something disturbs the soil. Ti can be construction, farming, or wind. When a person breathes the fungi into lungs, the infection occurs and causes fever, pain in the chest, and coughing. This is the acute infection that is usually resolved on its own. Valley fever is not transmitted from person to person.
Signs and symptoms of acute Valley fever
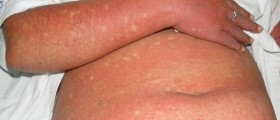
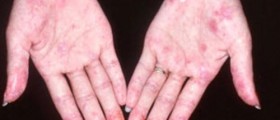
Valley fever is usually very mild and followed by a small number of symptoms. In some cases, the disease is completely asymptomatic. However, the initial acute infection may progress into a serious chronic disease if not treated on time. First symptoms of Valley fever are usually noticeable up to three weeks after the exposure to contaminated soil and air. At the onset of the disease, many patients may think they are actually having flu. The symptoms include fever, persistent cough, chest pain, night sweats and chills, feeling of tiredness and exhaustion, headache, shortness of the breath, painful joints, and may develop red rash. The rash is characteristic in appearance and looks like painful red bumps that typically turn brown after some time. The rash usually affects the lower legs, but it may also show up on chest, arms and back. People with these symptoms should seek medical help, especially if their symptoms are pronounced. If the initial infection doesn’t resolve it may progress to chronic form of pneumonia.Some patients will never experience any of the symptoms of Valley fever, and they may find out later in life, upon a blood test or routine chest X-ray examination, that they had been infected with these fungi. Usually, chest X-ray reveals small residual infections on the lungs, which look like tumors.
Risk factors
The most important risk factor for Valley fever is environmental exposure. It is estimated that up to half of the population living in areas where Valley fever is endemic, have been infected. People working and living close to earth and dust are at the highest risk. Pregnant women, elderly population, people with weakened immune system and people suffering from diabetes are at high risk of more serious forms of coccidioidomycosis.













Your thoughts on this
Loading...