Typhus is a contagious disease caused by Rickettsia typhi or Rickettsia prowazekii, infective agents contracted after one has been bitten by infected lice or fleas.
Rickettsia typhi is responsible for endemic typhus or Murine typhus, the infection that affects only some countries or certain parts of the world. Such type of the disease is not commonly reported in the United States. Endemic typhus is usually found in areas where hygiene is poor. Animals carriers of infective agents are rats, cats, opossums, raccoons and skunks.
Rickettsia prowazekii is a cause of epidemic typhus (Brill-Zinsser) disease, a mild form of the disease which most commonly affects elderly individuals and is actually a reactivation of the previously contracted infection. Lice, fleas and flying squirrels are carriers of this infective agent.
Typhus Clinical Characteristics
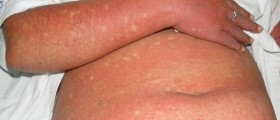
As far as Murine typhus is concerned, the infection is characterized by abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, headache and backache. Furthermore, patients complain about extremely high fever which may linger for up to 2 weeks, hacking/ dry cough and joint/muscle pain. The skin gets covered with rash which typically begins in the middle of the body and then spreads.
Epidemic typhus causes high fever with chills, photophobia, severe headache and muscle pain, joint pain and cough. There is also low blood pressure while patients may even develop delirium or stupor. Finally, there is rash affecting the entire body except for the palms and soles. Initially, rash is light red and may after some time become dull and red. Bleeding into the skin affecting small areas can occur as well.
Diagnosing Typhus
Blood tests show drop in number of red blood cells and platelets. It is also possible to confirm high lever of typhus bodies, low level of albumin, low sodium level and slightly elevated liver enzymes. Sometimes there is also abnormal function of kidneys in a form of mild kidney failure.
Treatment for Typhus
This infectious diseases is easily eradicated with potent antibiotics such as doxycycline, tetracycline and chloramphenicol. Tetracycline is not a drug of choice for children who are growing because it may stain teeth and also affect bone growth. Typhus patients are additionally administered intravenous fluids.
If typhus is left untreated, 10-60% of patients may die. The risk of lethal outcome is the highest in elderly individuals. But if antibiotics are administered, nearly all patients overcome infection without any complication. Complications, however, may occur and they include renal insufficiency, pneumonia and damage to the central nervous system.Prevention of Typhus
It is not possible to eradicate infection in endemic areas where hygiene is below standard. The infection, on the other hand, rarely occurs in case there is good sanitation and public health measures which successfully reduce the rat population.
Lice that are associated with epidemic typhus are killed by boiling clothes and avoiding wearing infested clothes for 5 days, using insecticides and with bathing.












Your thoughts on this
Loading...