
Acute HIV infection, also known as the acute seroconversion syndrome, is the second stage of the HIV infection that occurs right after the incubation period and prior to latency stage. HIV is the main cause of acquired immunodeficiency syndrome, known as AIDS. This severe disease affects a person's immune system and makes a patient prone to series of life-threatening infections.
Causes and course of HIV infection
The HIV virus is transmitted from an infected person to another by the exchange of the bodily fluids: blood, semen, vaginal fluid, pre-ejaculate or breast milk. HIV is most commonly transmitted sexually, trough contaminated needles and from an infected mother to her bay during the delivery or breastfeeding. The incubation period for HIV virus is most commonly asymptomatic and may last two to four weeks. The acute infection lasts approximately 28 days and is distinguished by numerous symptoms. Latency phase occurs right after the acute phase and lasts from two weeks to more than twenty years. In this stage, patient may not express any of the symptoms but it may eventually develop to AIDS.
Acute HIV symptoms
Acute symptoms of an HIV infection are similar in both males and females. Only in the later stages of the disease, when the complete hormonal balance in the body is disturbed, men and women experience somewhat different symptoms.
The first symptoms of the acute HIV infection are similar to the symptoms of common flu or mononucleosis. Approximately 80% to 90% of all individuals experience fever, swelling of the lymph nodes, sore throat, skin rash, extreme tiredness, mouth sores, headaches, nausea and vomiting. Some patients may have inflammation of the liver and spleen, weight loss and various neurological symptoms. These symptoms usually last less then two weeks.
The nature of the symptoms causes a frequent misdiagnosis. Even in the medical institutions, patients are often diagnosed as having flu.
Proper diagnosis and treatment of HIV
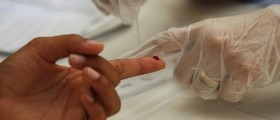
Symptoms of an acute HIV infection are insufficient for a proper diagnosis. Moreover, the symptoms may not be present at all. Proper diagnostic procedures involve HIV RNA testing. Antibody test may be falsely negative during the acute infection stage, because our bodies require approximately two months producing the antibodies.
Diagnosis of HIV infection requires an immediate action. Patients should be treated with antiretroviral medicines and they should take a series of preventive measures to stop the spreading of the virus. There is no vaccine or cure for HIV or Aids, therefore people at increased risk of contracting the virus should get tested to prevent the spread of the disease and start with the treatment on time.










Your thoughts on this
Loading...