
Pyogenic arthritis (septic arthritis) is acute suppurative inflammation of joints that develops due to different microorganisms that reach the affected joint via blood or directly enter the joint space after some injuries. It is also possible to develop pyogenic arthritis if the nearby bone is affected by osteomyelitis and infection spreads to the joint and all its components.
Pyogenic arthritis is frequent among premature neonates, children, elderly people and immunocompromised individuals. Although the inflammation usually affects only one joint (predominantly the knee or the hip) it may also affect several joints at the same time.
Pyogenic Arthritis Clinical Characteristics
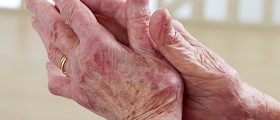
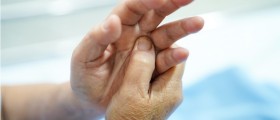
All symptoms and signs of joint inflammation develop rapidly. Infection is responsible for severe pain, swelling of the affected joint and sometimes fever accompanied by chills. In case the hip joint is affected, patients complain about pain in the groin area that intensifies while walking. The very joint is tender to touch. Apart from typical symptoms and signs of joint inflammation children may also feel nauseated and vomit.
Pyogenic Arthritis Causes
The very infections results from the spread of infective agents from the original site of infection to the affected joint. These may include different bacteria, viruses or fungi. Microorganisms may also enter the joint during surgical manipulation with the joint or due to joint injury. Gonoccocal infections are frequent among neonates, children develop pyegenic arthritis due to Haemophilus influenzae or Staphylococcus aureus while adults most commonly suffer from pyogenic arthritis caused by Streptococcus pyogenes, Staphylococcus aureus and Streptococcus viridans.
Pyogenic arthritis is considered a serious medical condition that needs to be treated promptly. Only this way severe damage to the joint and nearby bones can be prevented. Timely treatment also prevents abscess, blood poisoning and septic shock.
Pyogenic Arthritis Diagnosis and Treatment
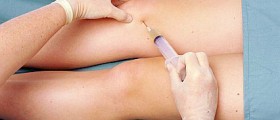
In order for pyogenic arthritis to be confirmed doctors investigate patient's medical history, perform a complete physical exam and conduct synovial fluid and blood tests. Samples of synovial fluid confirm the presence of microorganisms. Blood cultures and urine cultures may be of additional help in identifying the infective agent responsible for the condition. In fluid taken from the affected joint is negative, a person may need to undergo a biopsy of the synovial tissue.
As soon as the diagnosis is confirmed patients start treatment with potent antibiotics. These drugs are initially administered intravenously. This maneuver allows better effects and more efficient eradication of microorganisms. At some point patients continue taking antibiotics orally. In some cases patients undergo surgical drainage of the affected joint. Viral arthritis is treated with non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.
Most patients completely recover. Potential complications of pyogenic arthritis are osteoarthritis and joint deformity. Severe joint damage requires reconstructive surgery.
- www.nhs.uk/conditions/septic-arthritis/
- medlineplus.gov/ency/article/000430.htm
- Photo courtesy of www.scientificanimations.com via Wikimedia Commons: commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Rheumatoid_arthritis_-_Swollen_finger_joint.jpg



-Arthritis_f_280x120.jpg)

-Symptoms,-Diagnosis,-Treatment_f_280x120.jpg)








Your thoughts on this
Loading...