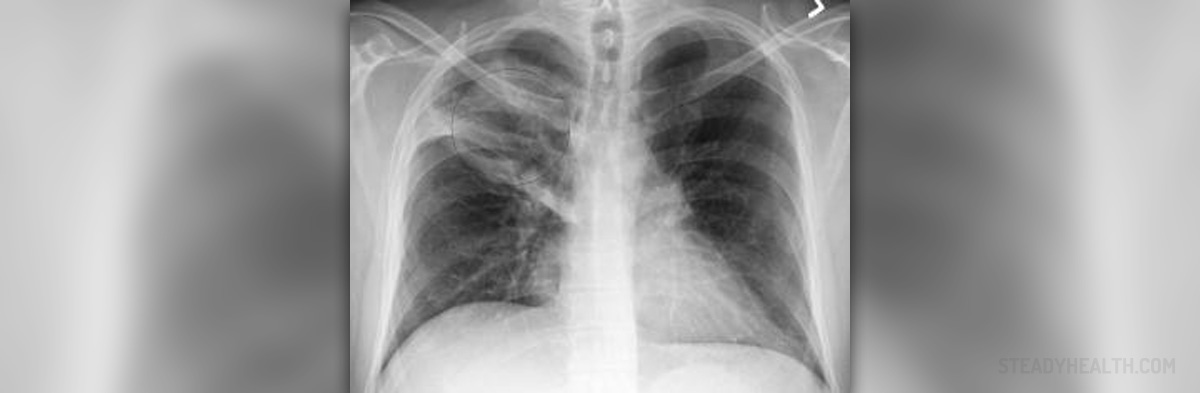
Bacterial pneumonia is a serious condition. It represents an inflammation of the lungs caused by bacteria. The condition typically features with fever, coughing, shortness of breath and chest pain.
In people suffering from bacterial pneumonia the weak immune system has allowed the bacteria to enter the lungs and start to multiply. Bacterial multiplication leads to inflammation of the lungs and characteristic symptoms of pneumonia. Namely, inflammation is always accompanied by extravasation of fluids into the alveoli. Accumulation of fluid leads to shortness of breath and inappropriate exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide. The very presence of bacteria is responsible for increase of body temperature and once the inflammation has reached the peak the person starts to cough. Chest X ray is a perfect tool for confirmation of pneumonia. Causes of Bacterial Pneumonia
As it is clear from the very name, bacterial pneumonia is always caused by bacteria. There are many types of bacteria that are capable of causing pneumonia. The most common infective agents that cause bacterial pneumonia are Streptococcus pneumonia, Hemophilus influenzae, Chlamydia trachomatis, Mycoplasma pneumonia and Legionella pneumophila. The infection can develop after the infective agents are inhaled or there is also a possibility for bacterial pneumonia to develop if the bacteria are spread from the other parts of the body. Some age groups are more susceptible to pneumonia. They include elderly people and children.
Clinical Characteristics of Bacterial Pneumonia
The condition features with specific symptoms and signs. Pneumonia develops quickly. The person suffers from high fever and chills. The cough is initially dry but one eventually starts to cough up mucus. The mucus is white, yellow or brown in color. There is also intensive chest pain particularly while coughing. And finally, patients suffering from bacterial pneumonia complain about shortness of breath.
Treatment for Bacterial Pneumonia
Bacterial pneumonia is treated with antibiotics. The actual antibiotic that is going to be prescribed depending on several factors such as whether the person is suffering from other medical conditions, if there are allergies to certain antibiotics or if he/ she is taking some drugs that may interact with the particular antibiotic.
It is essential to drink plenty of fluids. The excess of fluids will soften the mucus and make coughing up easier. In case of increased body temperature patients are prescribed anti-fever medications such as acetaminophen or ibuprofen.
Patients who are smokers must abstain from cigarettes until they fully recover. And finally, severe cases of bacterial pneumonia (severe shortness of breath, low oxygen saturation etc.) require hospitalization and supervised treatment. In hospitals all medications are generally administered intravenously.







-And-Breathing-Problems_f_280x120.jpg)







Your thoughts on this
Loading...