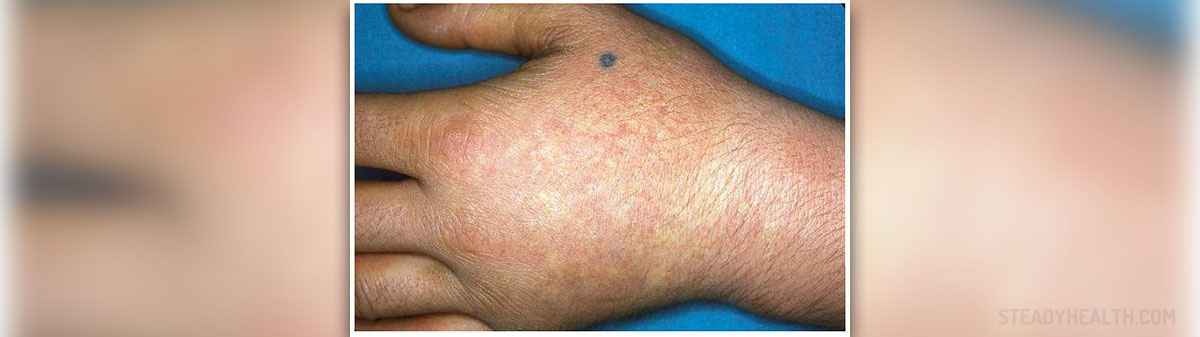
Paronychia is a medical term that refers to inflammation of the skin around nails. Acute paronychia is the most commonly reported hand infection in the Unites States. The infection generally affects children and results from nail-biting, quite nasty habit which may also be present among adults. Paronychia is classified into acute and chronic according to how long the infection lasts.
What Causes Paronychia?
Paronychia can only develop if there is previous loss of integrity of the skin around nails. So, any cut in the areal allows bacteria to enter, start to multiply and eventually include inflammation. Predisposing factors include problems such as a hangnail, ingrown nail and nail-biting. In majority of cases paronychia is caused by Staphylococcus aureus. The infection may also result from other pathogens such as Streptococcus species or Pseudomonas species. Chronic paronychia develops due to repeated irritation of the paronychium. Such irritation may be associated with prolonged exposure to harsh detergents, water or is closely related to Candida albicans or other fungal infection.Clinical Characteristics of Paronychia
The skin surrounding the nail gets inflamed. Inflammation is typically accompanied by skin redness, swelling and intensive pain. The affected area is warm to touch. Progression of the infection leads to accumulation of pus, hence the swelling may turn yellowish. Infection caused by Pseudomonas my cause accumulation of green pus. In severe cases of paronychia there is enlargement of the elbow or even armpit lymph nodes.
Chronic form of the infection is characterized by redness and tenderness of the skin. Still, both of these are not so intensive as it is the case in acute inflammation. Patients suffering from chronic paronychia may have boggy skin around their nails.
Diagnosing Paronychia
Paronychia is easily diagnosed just by taking medical history and after examination of the affected finger. If there is pus accumulation, doctors may take samples in order to identify the bacteria which has led to infection. This may not be necessary since many times the infection is caused either by Staphylococcus or Streptococcus species. Diagnosing chronic paronychia may be more challenging. Treatment for Paronychia
Acute infection requires application or warm soaks. This is supposed to done 3-4 times per day. Warm soaks may reduce the pain. Antibiotics are cornerstone of paronychia treatment. Doctors mostly prescribe cephalexin or dicloxacillin. Patients allergic to penicillins are prescribed antibiotics they are not allergic to. Pus collection and abscess require incision and drainage. Sometimes a small portion of the nail is removed.
Since chronic paronychia usually develops as a consequence of fungal infection, it is treated with antifungal medications.








_f_280x120.jpg)




Your thoughts on this
Loading...