
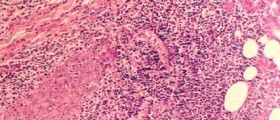
Sialadenitis is a medical term that refers to inflammation of salivary glands. The inflammation may be acute and chronic and sometimes is classified as recurrent. Sialadenitis may be caused by different infections or is associated with some autoimmune diseases.
Acute Sialadenitis
In order for one to develop acute sialadenitis there need to be some predisposing factors. Some of them are decreased flow of saliva and poor oral hygiene. Decreased production of saliva and its subsequent insufficient flow develops due to dehydration and may be associated with some surgeries or is a side effect of some medications. Acute sialadenitis also represents exacerbation of low grade chronic sialadenitis.
Patients suffering from acute sialadenitis complain about pain in the affected area. The inflamed gland is swollen which also leads to swelling of the surrounding soft tissues. The skin above the inflammation may be red and tender to touch. In severe cases swelling spreads from the affected area to the cheek, periorbital region or the neck. Some patients develop low grade fever and all of them experience malaise. In case of purulent inflammation, by pressing the inflamed salivary gland one may force out the pus which leaves the gland through its openings.Causes of Acute Sialadenitis
It is estimated that Staphylococcus species are the most common infective agents responsible for acute sialadenitis when it comes to bacterial infections. Furthermore, salivary gland inflammation may also be connected to different viral infections such as mumps, herpes virus infections and HIV infection.
In case the inflammation repeats (which is, for example, common in individuals suffering from salivary stones) acute sialadenitis may turn into a chronic form.
Diagnosis and Treatment for Acute Sialadenitis
Diagnosis of sialadenitis can be confirmed by a well experienced primary care physician or dentist. They investigate patient's medical history and perform complete physical examination as well as oral examination. Saliva and blood can be easily tested for the presence of bacteria. Viral infection responsible for sialadenitis can be confirmed thanks to typical clinical characteristics of the infection.
It is essential to rule out more serious diseases of the affected salivary gland such as tumors. This can be achieved by CT scan of the affected region.
Once definitive diagnosis is confirmed and the underlying cause of acute sialadenitis identified, patients are prescribed the most convenient treatment. Bacterial infections are treated with antibiotics and impeccable oral hygiene. Treatment for viral infections is only symptomatic. In some cases pain associated with acute sialadenitis may reduce after application of warm compresses. Severe infections as well as complications such as abscess are treated in hospitals.














Your thoughts on this
Loading...