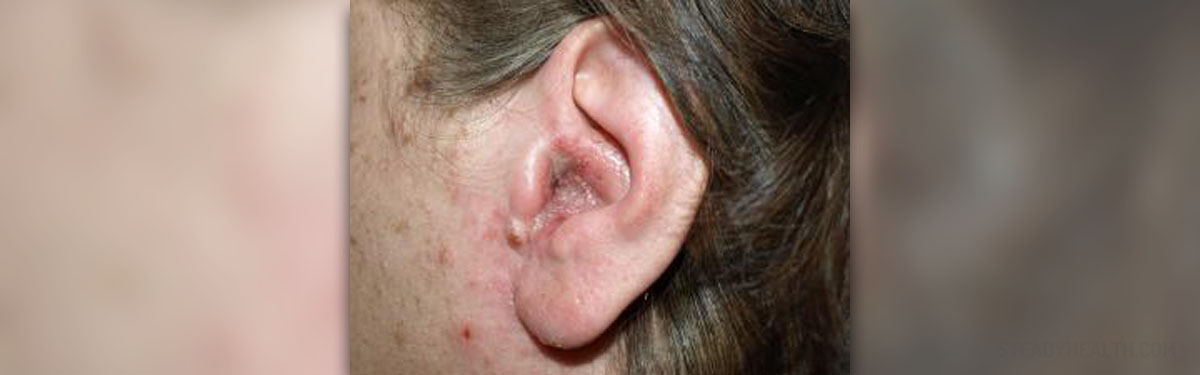
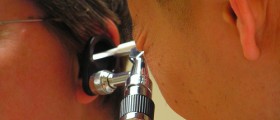
Acute otitis externa represents an inflammation of the outer ear and the ear canal. The main characteristic of the condition is inflammation of the skin of the ear canal. The infection may develop as secondary and aggravate the already existing dermatitis or eczema or it develops as a primary infection. Infective agents responsible for acute otitis externa are bacteria or fungi.
Clinical Characteristics of Acute Otitis Externa
In mild cases of acute otitis externa the leading symptom is pain. The intensity of pain actually correlates with the severity of inflammation. The pain increases if the outer ear is pulled or even touched. Tragus and antitragus (parts of the outer ear) are specially sensitive to touch. Apart from the pain otitis externa features with ear discharge and itchiness. In case of severe swelling or if discharge blocks the ear canal a person develops temporary conductive hearing loss. Itchiness of the outer ear commonly drives people to scratch the inside of the ear with slim implements which can only make the infection worse.
What Are Causes of Acute Otitis Externa?
Acute otitis externa is also known as swimmer's ear. As the very name suggests the condition can be connected with swimming in polluted water. However, it is also possible to develop the infection after a shower in case the water has been trapped in the ear canal. Furthermore, acute otitis externa may develop due to constriction of the ear canal by bone growth. In such case debris is trapped and is a source of infection. Otitis externa may be an occupations disease (saturation divers). Apart from the previously mentioned any kind of injury to the skin of the ear canal may be a perfect predisposing factor to infection. In order for the infection to develop there must be germs that may cause infection and loss of skin's integrity. This way infective agents penetrate the skin, multiply and infection eventually occurs.
Treatment for Acute Otitis Externa
There are two goals of otitis externa treatment. The first one is an eradication of the infective agents and the second one is restoring the health of the damaged skin. Patients should refrain from swimming or washing their hair until the infection resolves. Burow's solution is efficient against both, bacterial and fungal otitis externa. The cornerstone of the treatment, however, includes topical solutions or suspensions that come in a form of ear drops. There are different ingredients in such solutions and antibiotics, antifungal medications and anti-inflammatory steroids are only some of them. Prior to prescribing ear drops it is essential to examine the patient and check the eardrum. If the eardrum is perforated the usage of ear drops may have some side effects such as tinnitus, vertigo, dizziness and sometimes hearing loss.












Your thoughts on this
Loading...