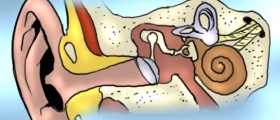
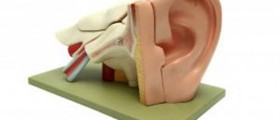
The ear comprises of three parts, the outer ear, middle ear and the inner ear. Each of them can be inflamed due to various reasons. Inflammation of the middle ear is medically known as otitis media. Serous otitis media represents inflammation of the middle ear accompanied by accumulation of fluid in the middle ear. The problem may be acute (only temporary) and chronic when inflammation tends to linger for a long period of time and frequently repeat.
Otitis media develops once the Eustachian tube fails to open (because of some infection or allergy) and allows the fluid to be properly drained into the throat. Accumulation of fluid leads to inflammation and may be the cause of secondary supurative otitis media in case it gets contaminated with bacteria.
In chronic serous otitis media there is either prolonged Eustachian tube blockage or thickening of the fluid inside the middle ear, both of which are potential culprits of all the accompanying health issues. One of potential complications is hearing impairment.
Serous Otitis Media: Causes
Problems with Eustachian tube opening may be congenital or acquired. Acquired conditions responsible for failure of the Eustachian tube to open include infections of the upper respiratory tract and certain allergies. Inflammation of adenoids is another common cause of serous otitis media in little children.
In certain number of children the Eustachian tube is rather small. They belong to a group of individuals with the familiar tendency to middle ear infection. Furthermore, children born with cleft palate are prone to serous otitis media because they lack the muscles that move the palate which are necessary for proper opening of the Eustachian tube.
Serous Otitis Media: Treatment
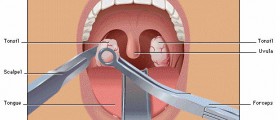
Treatment for acute serous otitis media includes treatment of the underlying conditions that have led to inflammation of the middle ear. So, by bringing infections of the upper respiratory tract and allergies under control, one may significantly benefit and symptoms and signs of serous otitis media soon withdraw. Doctors commonly prescribe decongestants, antihistamines and antibiotics. In case of complications such as abscess formation, the patient undergoes myringotomy (surgical incision made in the eardrum membrane).
Treatment for chronic serous otitis media is much more complex. All cases of recurrent upper respiratory infections and frequent flare-ups of allergies may induce repeated inflammation and chronic serous otitis media. Apart from conservative treatment with different mediations, doctor may opt for Eustachian tube inflation (a procedure that relieves congestion and reestablishes middle ear ventilation) or surgery.
Surgery for chronic serous otitis media helps in dealing with infection and prevents potential complications (e.g. hearing loss). Myringotomy removes the accumulated fluid from the middle ear. This procedure may be accompanied by insertion of a ventilation tube. Some children require surgical removal of adenoids. Once the infection is completely brought under control the ventilation tube is removed and in case the hole remains in the eardrum, it is surgically closed.






_f_280x120.jpg)



Your thoughts on this
Loading...