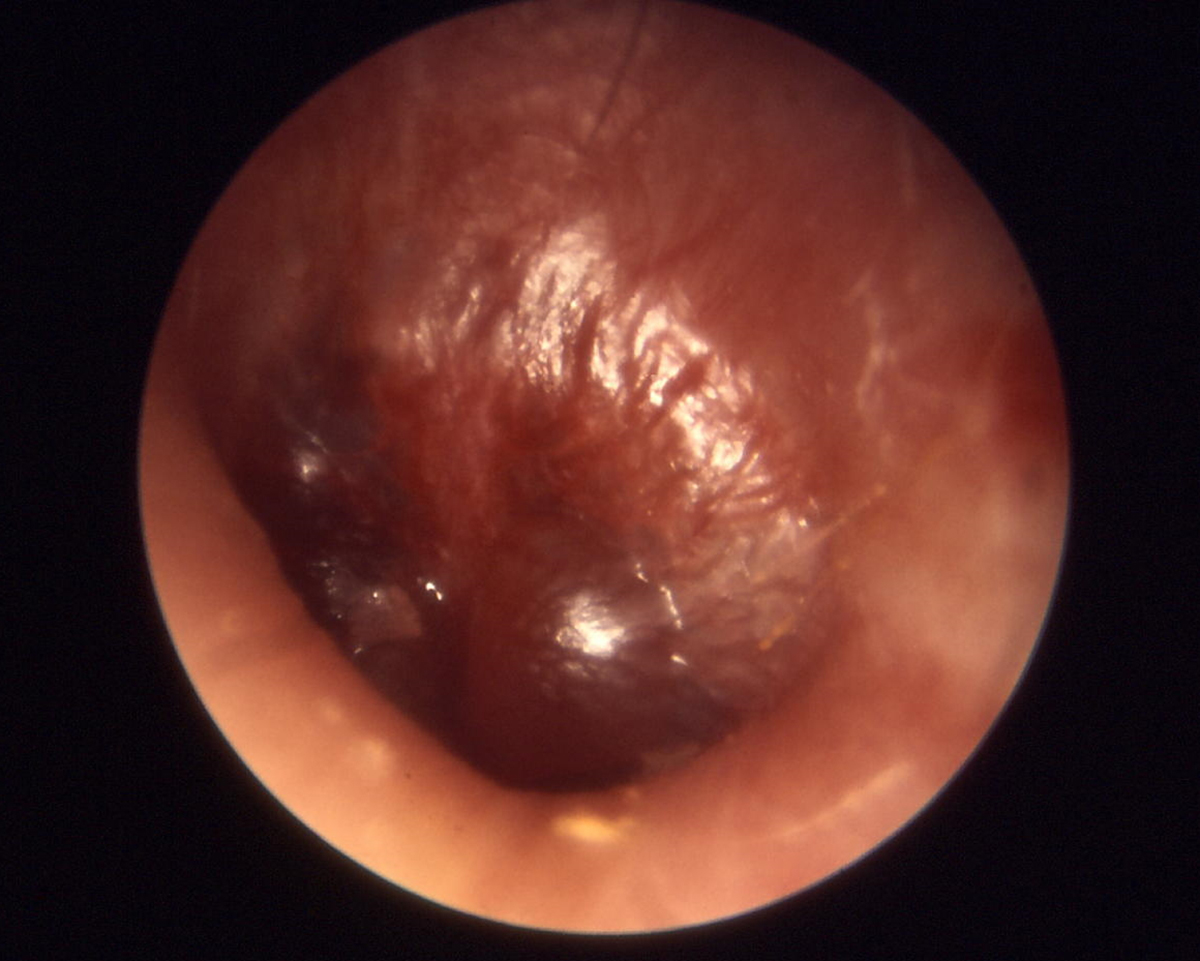
Definition of Otitis Media
Otitis media is the medical term most people commonly referto as inflammation of the middle ear. For those who do not know, the middle earis the space behind the eardrum which is in normal conditions filled with air.There are more than 20 million cases of acute otitis media each year in theUnited States.
What Causes Otitis Media?
Otitis media is in most cases associated with a malfunctionof the Eustachian tube. This organ is a small canal which connects the throatarea and the middle ear and it is in charge of equalizing the pressure betweenthe middle ear and the outer ear. When there are malfunctions it cannot drainthe fluids from the middle ear properly and it all results in the fluidbuildup. The buildup provides an excellent breeding ground for a large numberof different types of viruses, bacteria, fungi and other pathogens whichtrigger infections. The functioning of the Eustachian tube may be compromiseddue to a number of different factors such as a malformation of the tube,congestion and swelling of the lining of the tube, the throat and the nose,allergic reactions, common cold, absence of breastfeeding, spending time in adaycare setting, a weak immune system, family history of ear infections andexposure to cigarette smoke.
What Are the Different Types of Otitis Media?
There are two main types of otitis media and those includeacute otitis media and otitis media with effusion. Acute otitis media ischaracterized by abrupt redness and swelling which are also often accompanied byhearing loss, painful sensations in the ears and high fever. It is commonlyconsidered as a minor complication of sore throat, common cold or some othersort of upper respiratory infection. This type of medical condition is notinfectious, but the upper respiratory infections which accompany it usuallyare. Otitis media with effusion is completely different as it involves theaccumulation of the mucus and the fluids even after the alleviation of the initialinfection. The symptoms of otitis media usually involve inflamed eardrums,fever, painful sensations, ear drainage, vomiting, crying, hearing problems,irritability, scratching at the ear and tugging at the ear. Otitis media whichaffects all other age groups in most cases involves symptoms such as highfever, ear drainage, vomiting, nausea, loss of balance, dizziness, hearingproblems, feeling of pressure inside the affected ear and painful sensationsinside the ear. The most common symptoms of otitis media with effusion mayinvolve hearing difficulties, cough, runny nose, and sometimes even diarrhea.
Complications of Otitis Media
Otitis media may sometimes be associated with certain othermedical conditions and complications. A common ear infection may sometimes leadto minor instances of hearing loss. This hearing loss usually occurs due to thebuildup of fluids and mucus inside the Eustachian tube. If the pressure on theeardrum gets too excessive, it may lead to rupture in some cases. Most cases ofhearing loss induced by ear infections are temporary, but untreated cases maylead to permanent hearing loss as well. In cases of children, these nuisancesmay be associated with serious problems concerning the child’s language andspeech development.
Diagnosis
Otitis media is usually performed by utilizing two types oftests. A test called pneumatic otoscopy is commonly performed with aninstrument called otoscope in order to inspect the eardrum and the presence offluids. There is another test called tympanography which involves an instrumentcalled tympanogram. This test is performed mainly to examine the functioning ofthe Eustachian tube. The physician also looks for certain symptoms such asbulging eardrums, fever, ear pain, fluid behind the eardrum and other sorts ofsymptoms in order to determine that the person suffers from otitis media.
Treatment
Most cases of acute otitis media are commonly treated withcertain types of oral antibiotics, and the most frequently used one isAmoxycillin. Otitis media with effusion is usually much easier to treat andmost cases do not require the use of any prescribed antibiotics. The fluidaccumulations inside the middle ear usually go away on their own in no morethan 6 weeks. The biggest problem with antibiotics is that may sometimesinvolve certain side effects.
Means of Prevention
Otitis media can easily be prevented by following certainsimple guidelines. Babies should never be bottle-fed or breastfed while theylie down. Secondhand smoke needs to be avoided as much as possible. It is veryimportant to have very good handwashing practices in order to avoid alldifferent types of infections. Those who use tissues need to know that theyshould not be reused. It is also very important to cover the mouth and nosewhile coughing and sneezing in order to prevent the contamination of others.Annual vaccines against the flu are also highly recommended.
- www.hopkinsmedicine.org/health/conditions-and-diseases/otitis-media
- www.stanfordchildrens.org/en/topic/default?id=otitis-media-middle-ear-infection-90-P02057
- Photo courtesy of B. Welleschik by Wikimedia Commons: commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Otitis_media_incipient.jpg












_f_280x120.jpg)
Your thoughts on this
Loading...