The uvula is an elongated hanging piece of tissue that projects from the soft palate above the back of the tongue. It is a grape-shaped structure composed of mucus membrane, connective tissue and the muscle known as the musculus uvuae. The function of this muscle is to allow the uvula to change its shape and tighten up thus helping it to fill the space at the back of the throat.

Functions of the Uvula
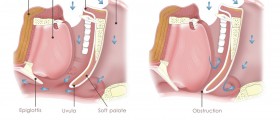
The uvula plays an important role in articulation of the sound of the voice thereby it assists with speech. Another important function of the uvula is to block the breathing passage during swallowing in order to prevent fluids and food from entering the nasal passages. The uvula is also involved in snoring.
Uvula Problems
Functions of the uvula can be affected by an infection or changes in the shape and size of this organ. Given below are common uvula problems:
VPI
VPI is short for velopharyngeal insufficiency, a condition characterized by nasal or hyper nasal speech. VPI occurs due to inadequate closure of the uvula against the back of the throat. This allows the air to escape through the nose instead of the mouth and results in speech impediment. A person with VIP can not properly pronounce certain consonants.
Nasal Regurgitation
During swallowing the uvula and soft palate block the nasopharynx to prevent food and fluids from entering the nasal passages. Failure of this closing mechanism can cause regurgitation of food and fluids through the nose, the condition known as nasal regurgitation. This condition is often seen in people affected by VPI, neuromuscular disorders or myositides.
Infection of the Uvula
Infection of the uvula can be caused by viruses or bacteria. This condition is known as uvulitis and is featured by expanding of the uvula 3 to 5 times its normal size. Symptoms of uvulitis include breathing difficulty, difficulty eating and talking. This uvula problem can be caused by dehydration, microbial infection, allergic reaction, inhalation of pollutants and excessive smoking.
Snoring
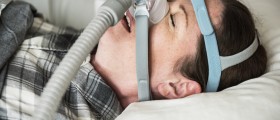
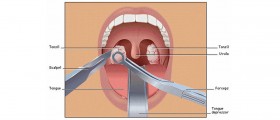
The uvula can cause snoring or heavy breathing during sleep and sometimes it may even contribute to sleep apnea. These problems can be caused by elongated uvula that may vibrate vigorously while sleeping. This can be treated with complete or partial surgical removal of the uvula. The procedure is known as uvulopalatopharyngoplasty (UPPP). However, this intervention can successfully reduce the symptoms in only 40-60% of all cases. The risk of sleep apnea reversal after surgical removal of the uvula still remains.











Your thoughts on this
Loading...