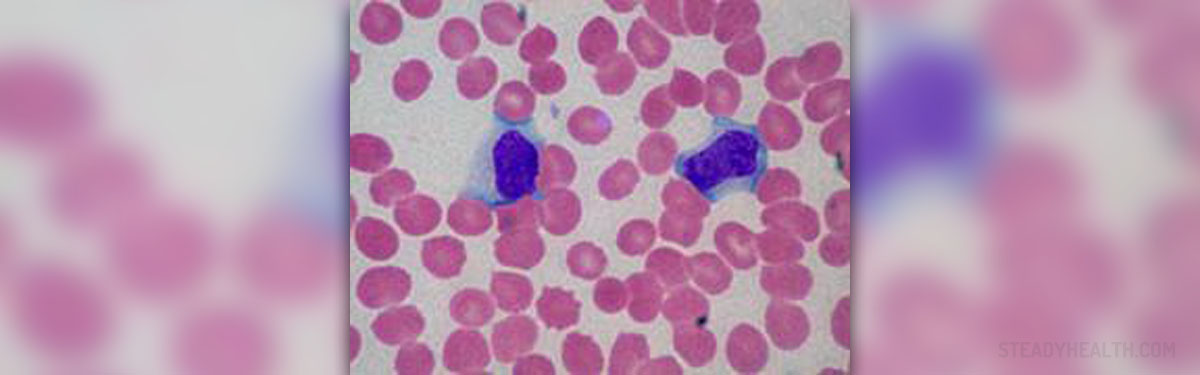
Lymphocytes are a type of white blood cells, normally present in everyone’s blood. Their function is to protect humans from microorganisms who want to invade the body and because of that lymphocytes are important part of human immune system. With the help of these blood cells our body is able to fight against different viruses and also against the growth of tumors inside the body. These cells are produced in the bone marrow. They could live for several weeks or years, but some lymphocytes can be of same age as the person.
Lymphocyte Types
There are 3 main types of white blood cells, called T cell lymphocytes, B cell lymphocytes and NK cell lymphocytes. Every type of lymphocytes has different role in the organism, but together they create strong immune system. B and T cell lymphocytes are proven to control the growth of cancerous cells and NK (natural killer) cells are able to kill many harmful cells and microorganisms in the body.
Whether there is low or high amount of lymphocytes in the body, abnormality in their number always suggests there is something wrong and the body is experiencing some problem. Under normal circumstances, the white blood cells contain some 15 to 40% of lymphocytes. If there is increase of lymphocytes over 40% of total amount of white blood cells this condition is known as high lymphocyte count or lymphocytosis. Decrease amount of these white blood cells is also problematic and this condition is called lymphocytopenia.
High Lymphocytes in Blood
Most laboratories take as standard and normal amount of lymphocytes in the blood to be about 1200 to 3200/ml (per milliliter). Always consult your doctor to determine your lab results, for he or she will be able to read them properly.
Different infections of the body may be the cause of lymphocytosis, especially chicken pox, rubella, mumps, toxoplasmosis and brucellosis (animal infections) or herpes simplex infection. Flu and whooping cough may also provoke increase in amount of lymphocytes present in the blood.
Acute and chronic lymphocytic leukemias (ALL and CLL) are also known to increase lymphocytes. Mononucleosis, hepatitis or cytomegalovirus infection of the stomach and eyes can also be blamed for increased amount of these white blood cells.
Use of certain medications and blood transfusions might raise the level of lymphocytes in the blood as well.
Diseases such as ulcerative colitis or inflammatory bowel disease (IBS) or Crohn’s disease can be the reasons behind increased number of these blood cells. Other reasons that may be responsible for the raise of lymphocytes include: inflammation of blood cells (vasculitis), some autoimmune disorders and plasma cell cancer like multiple myeloma.













Your thoughts on this
Loading...