Aseptic technique is a procedure performed under the sterile conditions. The goal of different aseptic techniques is to keep the patients free from hospital micro-organisms and other ways of contamination. Aseptic techniques are therefore used to prevent contamination of wounds and other sited on the body, and to ensure that only sterile equipment and fluids are used during the surgical procedures and other hospital treatments. Aseptic technique is therefore used to maximize and maintain asepsis, which is defined as a state of being free from disease-causing contaminants or preventing contact with microorganisms (bacteria, viruses, fungi and parasites). There is no definite way to eliminate all of the contaminants from the environment so the true goal of asepsis is the elimination of infection, and not sterility.
Aseptic technique in the hospital
Aseptic technique can be used in any clinical setting where the patients are at increased risk of contamination and infection. Certain patients may be highly vulnerable, especially if they have extensive burns, big wounds or suffer from immune system disorders. Typically, aseptic techniques are employed during the surgery and on the insertion of various medical utilities such as intravenous lines, urinary catheters, and drains.
Asepsis in the operating room
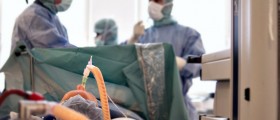
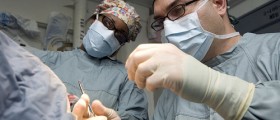
Aseptic technique is of major importance in the operating room. Surgical procedures always involve disruption of skin and exposure of underlying tissues. For this reason, aseptic techniques are used to prevent and minimize any chance of infection. Human body is a host for many microorganisms that normally live on the human body without causing disease. However, problems may arise when this endogenous flora gets into the contact with exposed tissues, during the surgery. For this reason, patients are required to shave their hairs from the sites of incision, and their skin is cleaned with potent disinfectant.
Doctors also need to undergo preoperative practices and procedures. Hand washing is an important stage of preparations that significantly reduces the spread of microorganisms. Proper hand washing includes removal of jewelry, avoidance of contact with the sink, and vigorous friction and scrubbing with long-acting, powerful, antimicrobial soap. The hand washing procedure should last at least two to five minutes.
Surgical team should also wear protective gloves, face masks, goggles and face shields. All of the drapes and linens placed on the patient also need to be sterile, as well as the surgical equipment used during the surgery. Surgical instruments are properly sterilized by chemical treatment, radiation, gas, or heat. All members of the surgical team, without exception, should demonstrate a good aseptic technique in the operating room.
- www.cdc.gov/injectionsafety/providers/provider_faqs.html
- www.cdc.gov/injectionsafety/PDF/FAQs-Safe-Practices-for-Medical-Injections.pdf
- Photo courtesy of SterilAir AG by Wikimedia Commons: commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Aseptikraum_sterilAir.jpg











Your thoughts on this
Loading...