What is tarsalcoalition?
What is tarsal coalition?
This is an inborn (present at birth, as it occurred duringfetal development) condition. It affects the bones of the foot in both childrenand adolescents. It is characterized by failure of the bones in the feet to separateduring fetal development which can cause the foot to be painful, stiff andflat. About one percent of the population has a tarsal coalition, which meansthat this condition is not very common, but neither is it rare.
What part of the foot is affected by tarsal coalition?
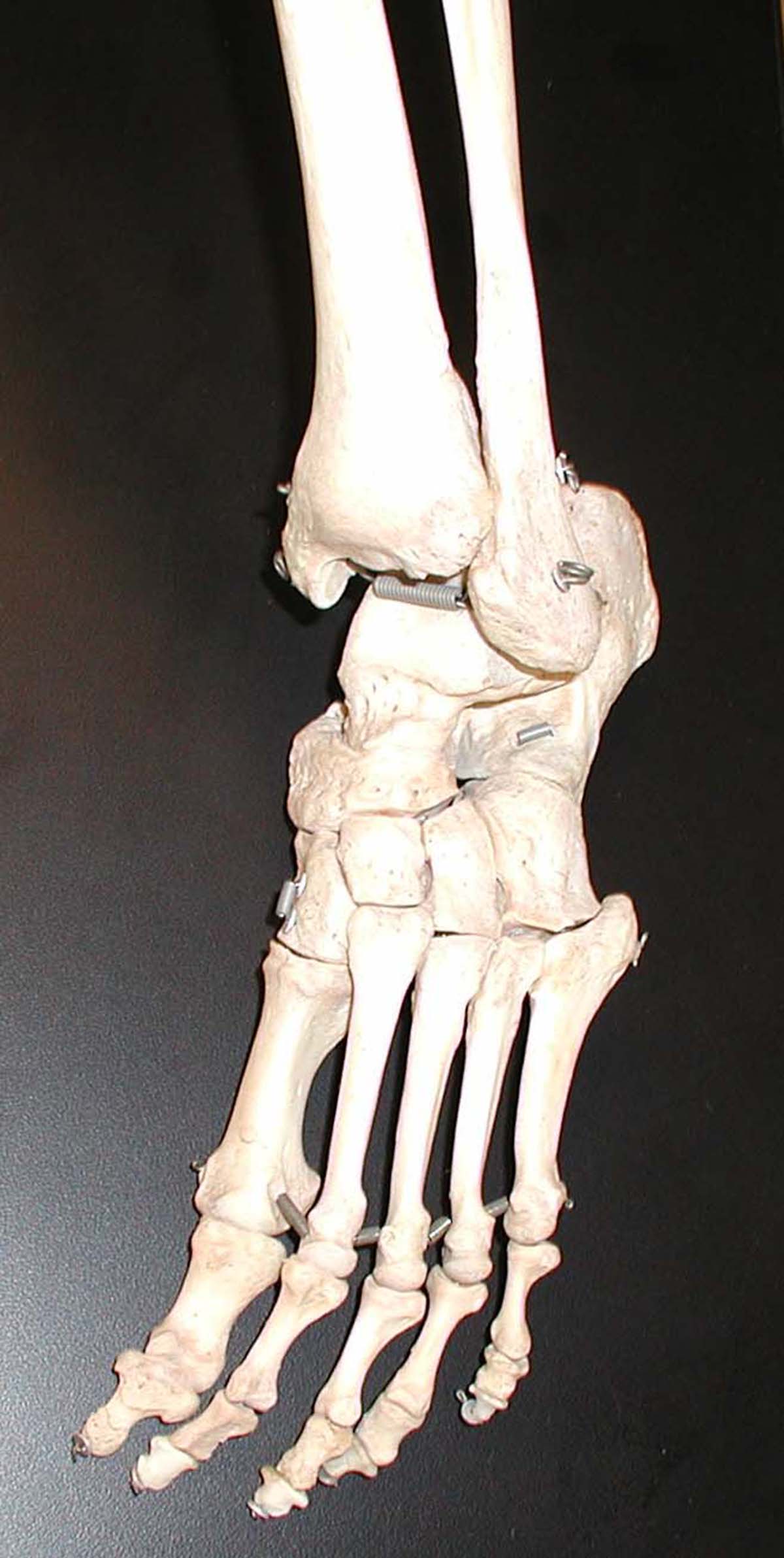
This condition affects any of the tarsal bones. These arethe seven bones that form the heel and the middle part of the foot. Two mostcommon types of tarsal coalition are the calcaneonavicular coalition and thetalocalcaneal coalition, where calcaneus, navicula and talus are Latin names ofthe affected tarsal bones. Name indicates which two bones did not separate.Sometimes, the term "bar" is used instead of "coalition" asit indicates that there is an unusual bar between the affected bones. The bar neednot be fully formed, and it can be made of bone, cartilage, or fibrous tissue,which will affect the stiffness of the bar.
Why is this troublesome?
The foot is a highly complex structure. It is responsiblefor adequate contact with the ground; transfer of forces that enable us towalk, and for dampening of the impact that is natural in every kind of motion.If all this is to work as it should, all of the bones of the foot must move inan adequate relation to each other. Abnormality or lack of motion between anytwo bones of the foot affects the entire foot and leads to increased stress inother joints in the foot, which will increase wear and tear in them and lead topain.
Symptoms and diagnosis
The primary symptom caused is pain, which is typically felton the outside of the foot, below that large bony protrusion on the outside ofthe ankle. Advanced condition affects other joints and in such cases pain maybe felt on the top of the foot and on the outside of the foot. Diagnosis isdetermined by history and physical examination. Areas of tenderness andrestriction of motion in each of the joints in the foot will be observed inparticular. An X-ray exam is very helpful for overview of the situation in thefoot, but the CT scan is regarded as the best tool. MRI scan is used if thecoalition is made of soft tissue.
Surgery and recovery
Surgery is used to remove or excise the bar and to restorenormal motion between the two bones as much as possible, or to fuse theaffected joints together solidly. Excision works better for younger children,whereas a fusion may be necessary in adolescents and older children.
Recovery after the excision procedure is quicker as there isno bone to heal together, and any kind of activity, if not painful, is allowedsoon after the surgery. On the other hand, the bones will need to heal togetherand fuse after the fusion procedure. Screws or metal pins are commonly used tohold the bones together until they heal, and use of a cast or brace isrecommended. Weight bearing may be delayed up to six or eight weeks..












-Symptoms,-Diagnosis,-Treatment_f_280x120.jpg)
Your thoughts on this
Loading...