Superior Limbic Keratoconjunctivitis
Superior limbic keratoconjunctivitis represents chronic, localized inflammation of the superior bulbar conjunctiva. The process of inflammation basically affects the superior limbic which leads to adjacent epithelial keratitis and papillary hypertrophy of the upper tarsal conjunctiva.
The exact cause of the disease is still unknown but it is believed that superior limbic keratoconjunctivitis develops as a consequence of inflammation due to soft tissue micro trauma. As a result of chronic inflammation of the conjunctive, it becomes thicker and keratization occurs. Final reaction to inflammation includes filamentary response. Superior limbic keratoconjunctivitis most frequently affects people suffering from thyroid eye disease, tight upper eyelids and prominent globes. Additional cause of superior limbic keratoconjunctivitis is scarring of the palpebral conjunctiva in euthyroid patients. Risk factors also include reduced volume of tears and prolonged closure of the eyelids.
This medical condition may withdraw completely but only after prolonged clinical course. It predominantly affects women and is most common in middle-aged people.
Symptoms of Superior Limbic Keratoconjunctivitis
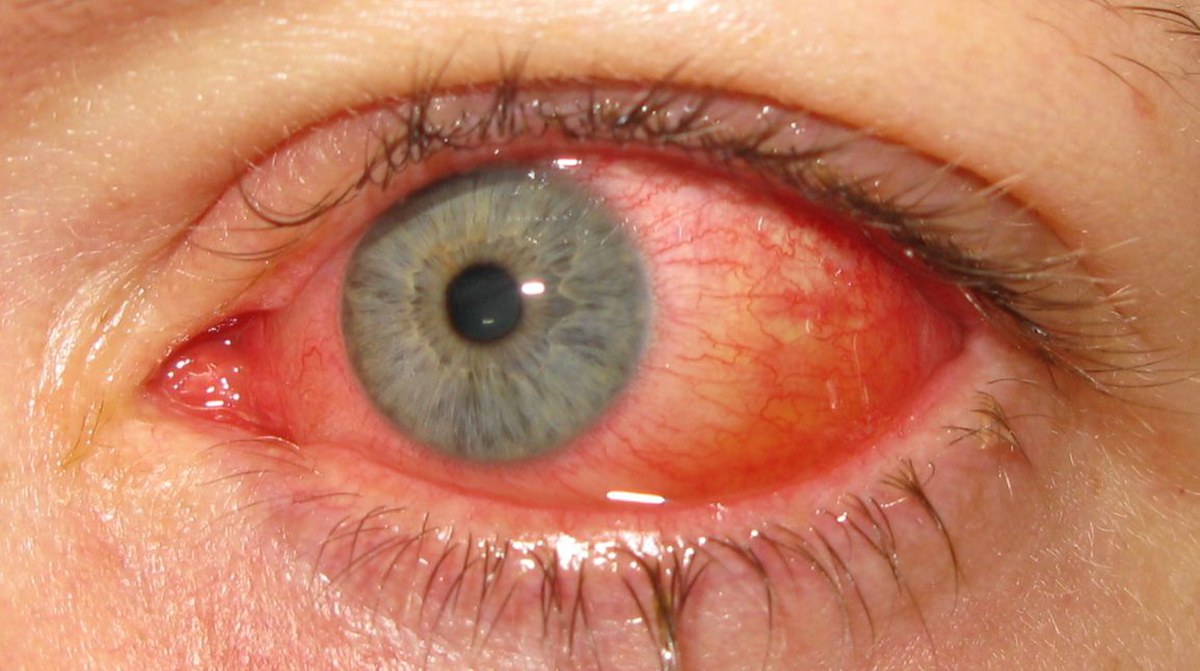
Patients suffering from superior limbic keratoconjunctivitis usually complain about irritation of the eyes and burning sensation. Affected eyes may be erythematous. In some patients the symptoms of the disease can be partially alleviated by moisturizing medications. The basic characteristic of symptoms is that they tend to reoccur and exacerbate and they also vary in intensity.
In majority of patients both eyes are affected by the process of inflammation. Corneal filaments are symptomatic for the disease and they make setting of the diagnosis rather easy.
Apart from the previously mentioned, patients who are suffering from thyroid gland disorder also complain about symptoms of the primary disease.
Diagnosis of Superior Limbic Keratoconjunctivitis
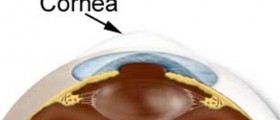
Diagnosis of superior limbic keratoconjunctivitis can be set after physical examination. Typical clinical findings include inflammation of the upper lid tarsal conjunctiva, adjacent inflammation of the upper bulbar conjunctiva and punctate rose bengal staining of the cornea. The affected conjunctiva is thick and hyperemic.
Surgery for Superior Limbic Keratoconjunctivitis
Apart from symptomatic treatment which includes proper lubrication, large diameter bandage contact lenses, pressure patching and topical trans-retinoic acid, patients can significantly benefit from surgery. Furthermore, the doctor may perform thermal, or silver nitrate cauterization of the superior bulbar conjunctiva.
Surgery for superior limbic keratoconjunctivitis includes recession and resection. The surgeon performs excision of superior bulbar conjunctiva. What follows is transplantation of amniotic membrane which is performed with the assistance of fibrin glue and final step of the surgery is corneal epithelial debridement. The procedure is done under local, retrobulbar or peribulbar anesthesia. Some patients require general anesthesia.















Your thoughts on this
Loading...