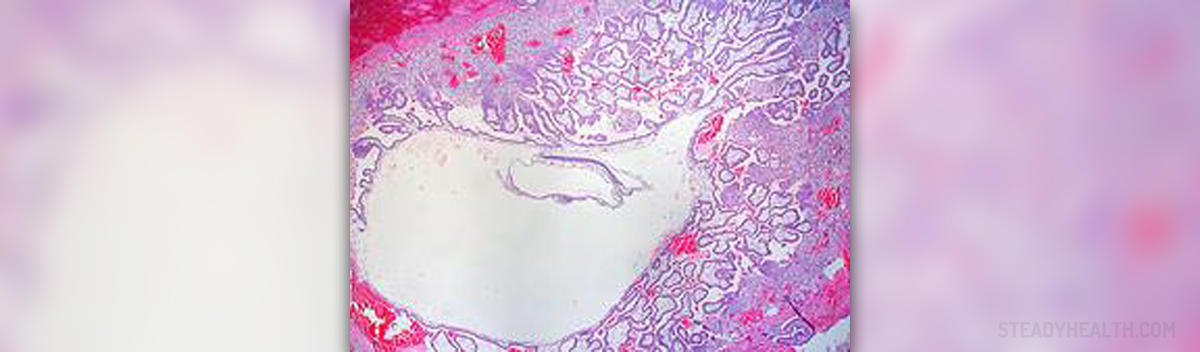
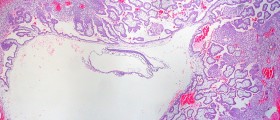
Ectopic pregnancy is a term that refers to implantation of a fertilized egg somewhere else in the pelvis instead of its implantation inside the uterus. Normally, once the egg is fertilized inside the fallopian tubes, it goes into the the uterus where it is supposed to be implanted. However, under certain circumstances, a fertilized egg may implant in the fallopian tube, ovary or other organs/tissues in the pelvis which may cause serious and sometimes even life-threatening complications.
Since approximately 95% of all ectopic pregnancies actually occur in the fallopian tube, they are commonly known under the name tubal pregnancies.
Ectopic Pregnancy Causes
Even though fertilized egg may get implanted somewhere else beside in the uterus, it simply cannot develop properly because the environment for growth and development of the egg requires specific conditions. It is normal for the egg to bury itself deep into the uterus. Still, if this occurs in other organs of the pelvis, such invasion is accompanied by serious health complications. Namely, invasion of the egg deep into the affected organ is accompanied by bleeding. Bleeding is initially mild and may become quite severe. Also, since fallopian tubes simply cannot provide with sufficient space for the embryo and they cannot expand adequately, at some moment they rupture.
In majority of cases ectopic pregnancy develops due to some blockage of the fallopian tube. The egg cannot pass through the fallopian tube and reaches uterus so implantation takes place in the fallopian tube instead of the uterus.
The risk for ectopic pregnancy is higher in women over the age of 35 as well as those who are suffering from certain hormonal imbalances. Vaginal douching is another risk factor for ectopic pregnancy.
Finally, any scarring (after surgery, infections or scarring associated with certain types of IUDs for birth control) may prevent a fertilized egg from reaching the uterus.
Ectopic Pregnancy Symptoms and Signs
Initially symptoms and signs of ectopic pregnancy are quite similar to those of normal pregnancy. For instance, there may be tenderness in breasts, absence of period, morning sickness etc. These symptoms and signs cannot help distinguishing normal from ectopic pregnancy in the early stage.
However, once the embryo reaches a significant size a woman develops more complex and quite bothersome symptoms and signs. Some of them are abdominal cramping and severe abdominal pain which may radiate towards the lower back. Bleeding, particularly if it is severe enough may cause circulatory collapse and drop in blood pressure. This subsequently leads to fainting and dizziness. Signs of advanced ectopic pregnancy are also quite similar to signs of appendicitis so it may be hard to differentiate the two. Differential diagnosis additionally includes urinary tract problems, stomach pain during pregnancy and some other gynecological issues.
Only in case ectopic pregnancy is detected in early stages it can be successfully terminated with medicamentous treatment. If it has progressed, the woman is treated surgically.








Your thoughts on this
Loading...