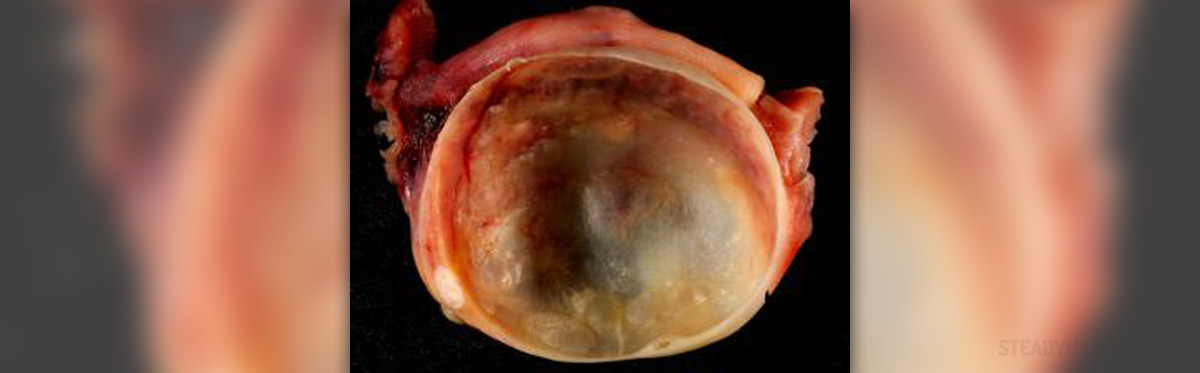
Each month a cystic structure called a follicle is formed on the ovary. The formation of this cyst is normal and represent maturing of the ovum that is eventually released and is ready to be fertilized. However, it may happen that the follicle keeps on growing and does not burst releasing an ovum. In this case we are talking about ovarian cyst.
Ovarian cysts commonly affect women in their reproductive years. They are usually asymptomatic and discovered accidentally during routine pelvic ultrasound examination. Fortunately, many ovarian cysts resolve on their own and there is no need for any intervention.
Ovarian cysts can be easily classified as simple or complex cysts. Simple ovarian cysts contain fluid while complex ovarian cysts apart from fluid also contain solids. Functional and follicular cysts are simple ovarian cysts while dermatoid cysts, endometriomas and cystadenomas represent complex ovarian cysts.
In case the cyst lingers and continues growing it may eventually rupture and cause serious complications. Symptoms of Ruptured Ovarian Cyst The very presence of the ovarian cyst leads to a constant or intermittent dull ache in the pelvic area, irregular menstrual cycles, pain in the pelvis shortly before and after the menstrual cycle and pain during sexual intercourse.
The symptoms of ovarian cyst rupture may vary significantly among women. Still there are several symptoms and signs of ruptured ovarian cyst characteristic for all women. They include nausea, vomiting and sometimes breast tenderness. Furthermore, a woman may complain about heaviness or fullness in the abdomen or pressure on the rectum or bladder.
Treatment for Ruptured Ovarian Cyst
Treatment for ruptured ovarian cyst generally depends on the severity of the condition. It is essential to estimate the damage and act promptly. All potential complications associated with rupture of the cyst must be prevented.
The first thing a doctor does is stabilizing the patient. He/ she evaluates the airway, breathing and circulation. The confirmation of the cyst rupture is achieved with ultrasound of the pelvis.
Once a patient is stabilized the doctor continues with certain tests. He/ she performs abdominal examination and there is also a need for surgical or laparoscopic exploration that is helpful in both, diagnosing and treating ruptured ovarian cyst. Hemorrhagic cyst always requires surgical management.
After the surgery all the patients are given a suitable postoperative care. The dietary regimes as well as specific exercises are recommended by the doctor. Women who have undergone ovarian cyst rupture and have been treated surgically must abstain from using tampons and sexual intercourse for some time.
Even after a woman is discharged she must be monitored and have regular consultations and further ultrasonography. It is essential to rule out potential malignancy and never mistake a benign cyst of the ovary for a malignant tumor.













Your thoughts on this
Loading...