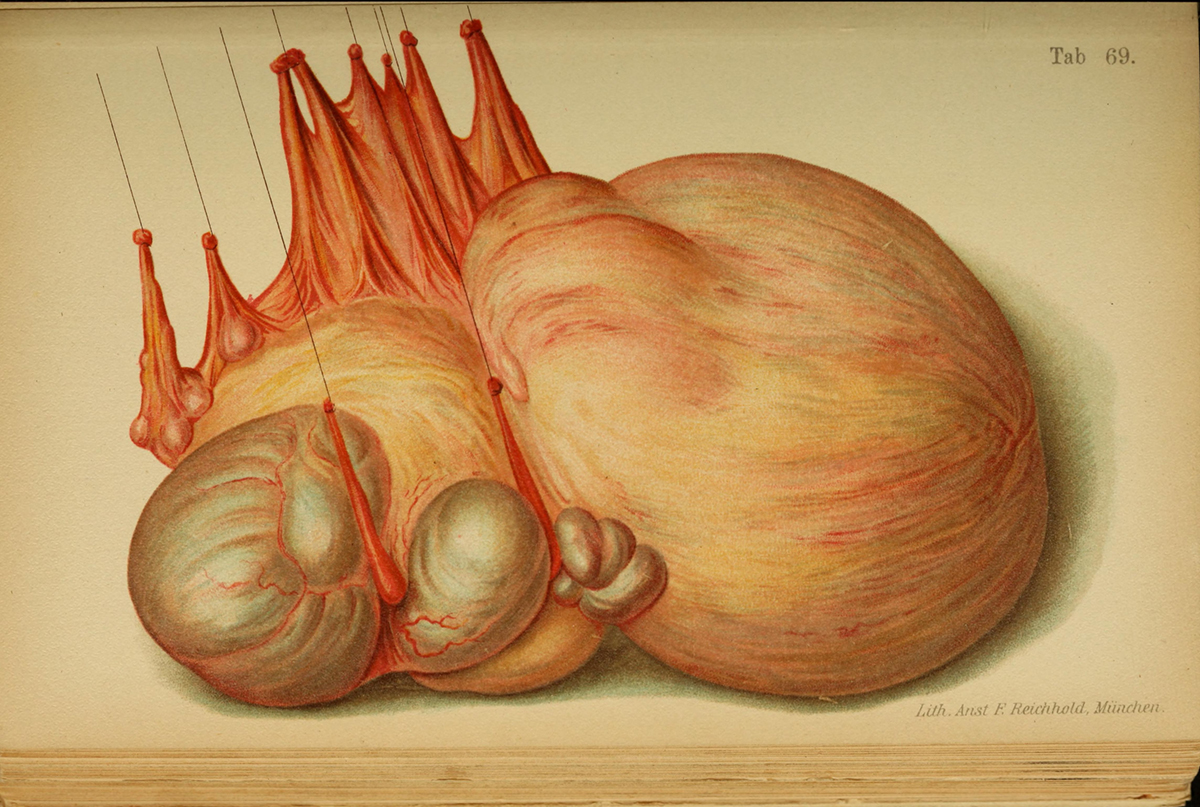
Ruptured ovarian cysts are relatively common in menstruating women. The rupture can be asymptomatic and women sometimes do not even know it happened, but it can also be more severe and cause quite a concern.
When the doctor diagnoses an ovarian cyst, he or she usually recommends biopsy which will confirm the cyst is not malignant. The cyst should then be monitored, because if it ruptures, it can cause severe pain, infection and hemorrhage.
Indications of ovarian cysts
Ovarian cysts are usually discovered during the pelvic exam. If the doctor suspects there is one or more cysts, he or she will probably monitor it over a month or so, using the ultrasound. If the cyst is still there after one month, it may require further examination. This is particularly the case if the cysts cause symptoms like painful and irregular periods, pain during bowel movement, pain during sex, general feeling of tenderness in the lower abdomen, which can even spread to the thighs and the buttocks.
However, problems can occur if the cyst is not causing any symptoms. In that case the patient is not aware of suffering from ovarian cysts, she does not seek treatment and it can potentially lead to serious complications.
Diagnosing the rupture of ovarian cysts
A ruptured cyst causes very sharp and intense pain in the abdomen. The pain is usually so intense that the woman suffering from it seeks immediate medical attention. The doctors in the emergency room perform a physical exam and also do blood tests, focusing particularly on the hematocrit levels. If those levels are abnormal, they may indicate an internal bleeding, which is always dangerous.
A pregnancy test is also performed in most emergency rooms and hospitals when the symptoms indicate ovarian cysts. This is because ectopic pregnancy is often linked with ruptured ovarian cysts. Another diagnostic means used in this case is urine test, performed to check for blood, puss, and signs of infection or inflammation.
In any case, doctors will stabilize the patient’s condition until all the tests are done, and then will inform the patient about the diagnose. In the follow up, the patient and the doctors will discuss together the treatment options.
The most important thing when it comes to ovarian cysts is to have frequent check-ups at the gynecologist’s office, because it is the only way to diagnose the cyst early and to prevent complications that may arise from the rupture. If cysts do exist and are correctly diagnosed, then it is important to have them monitored frequently by the gynecologist.










Your thoughts on this
Loading...