What is a Prolapse?
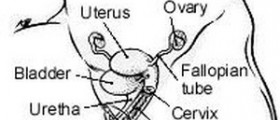
Prolapse of the uterus is a medical condition in which the structures of the vagina and the uterus get weakened and move down the vagina towards the vulva. The condition affects a largenumber of women so it can be considered as a fairly common one. Theaforementioned structures get damaged so the condition gradually develops.There are numerous factors which may lead to the development of a prolapse andthese include the natural process of aging, obesity, chronic cough,constipation, straining and lifting heavy objects. In some instances prolapsemay be associated with childbirth. Some cases may also be connected to genetic weakness of the tissues which are in charge of supporting the uterus orthe vagina. The most common symptoms of this uncomfortable medical conditionmay include a feeling of fullness in the vagina or a sensation which may bedescribed as a dragging one.
What is a Vaginal Hysterectomy?
Vaginal hysterectomy is a certain type of surgical procedurewhich involves the removal of the uterus through an incision in the vagina.This type of surgery is in most cases accompanied by sling and bowel proceduresfor urinary incontinence and prolapse repairs of the bladder. Not all cases of prolapse of the uterusrequire a vaginal hysterectomy as there are also certain alternatives tosurgery which may sometimes be helpful. This is mainly due to the fact thatthere are different degrees of prolapse. One of the most commonly utilizedalternatives to vaginal hysterectomy is physiotherapy. In some cases it is usedin conjunction with certain types of devices inserted into the vagina which areexceptionally efficient in improving its muscle tone. Other alternativetreatment methods include vaginal pessary which is a plastic sort of devicewhich serves a purposes of holding the prolapse up. Some cases may also berelieved by utilizing specially designed pelvic floor exercises.
How is a Vaginal Hysterectomy Performed?
Vaginal hysterectomy needs to be performed in a hospitalsetting and it requires either spinal or general anesthesia, which may sometimes be accompanied by sedation. The surgeon first needs to make a cutaround the cervix, before carefully pushing the bladder and the bowel away fromthe uterus. The next step of the surgical procedure involves clamping, cuttingand tying the blood vessels that supply the uterus and all the surroundingtissues. The uterus then gets removed and the vaginal vault gets closed. Somecases of vaginal hysterectomy may involve the use of additional supportingstitches to the vaginal vault. Once the surgery is performed, the patient isreturned to the ward where the nursing staff checks the vaginal bleeding, thetemperature, respiration, pulse and blood pressure of the patient. Thepatient needs to move onto alternate sides every two hours in order to preventpressure sores from occurring on the heels, the bottom and the back. One alsoneeds to take a really deep breath every hour in order to prevent any chestinfections from developing. The patient will also receive an absorbent dressingin the vagina which is very efficient in preventing any excessive bleeding.Some patients may receive a catheter as well in order to be able to pass the urinemuch more easily.
Complications of Vaginal Hysterectomy
Even though vaginal hysterectomy is in most cases completelysafe, it may still be associated with certain types of complications. One ofthe possible complications includes the urinary retention which may occur in acouple of days after the surgery has been performed. Due to difficulties inpassing urine, the patient may need to use a catheter in order to pass itnormally. Some cases of vaginal hysterectomy are involved with injuries tocertain adjacent organs such as the rectum, the ureters or the bladder. Somerare cases may also involve the development of a vaginal fistula. Among themost dangerous complications of vaginal hysterectomy are different sorts ofinfections. Antibiotics are commonly used before and after the surgery in orderto prevent infection, but there are still small chances of the development of pelvicor vaginal infections. Such types of infections may easily be detected bysymptoms like fever, an unpleasant smelling vaginal discharge and burning orstinging sensations when passing urine. Some rare cases of vaginal hysterectomymay involve severe blood loss and hematoma. The cases in which hematoma occurs areusually taken care of by utilizing surgical drainage, while blood loss may becompensated for with blood transfusion. Embolism or blood clots in the legs orthe lungs are a pretty much rare risk in pelvic surgery and even if they dooccur, they may be relieved by utilizing certain types of blood thinning agentsor support stockings. Most surgical interventions require the use of modernanesthetics and there are certain problems associated with those which may alsotake place in some cases of vaginal hysterectomy.














Your thoughts on this
Loading...