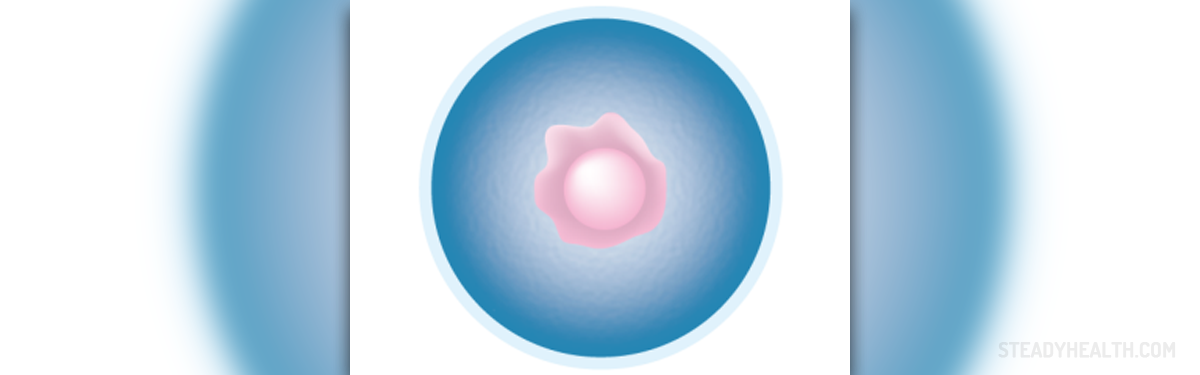
Chromosomal problems are the most common culprit when the body recognizes problems in the embryo's chromosomes, it automatically reacts by halting its development, because the embryo could not continue to form into a well-functioning baby. For many women with an anembryonic pregnancy, miscarriage symptoms soon become noticeable. A missed menstrual period and a positive pregnancy test are often followed by vaginal bleeding, cramps, and abdominal pain. In other cases, women will not even know they were pregnant and will simply experience a "late period", which is in reality a very early miscarriage.
Sometimes, a miscarriage will not take place, and a woman will experience early pregnancy symptoms like morning sickness and extreme fatigue, just like with a healthy pregnancy. In such a case, the first ultrasound will lead to a diagnosis when the technician notices that a sac is developing without an embryo inside. In either case, there are two treatment options. The first one is waiting for the body to start the process of miscarriage naturally, and the second is to opt for a D&C. A blighted ovum cannot be prevented. Most women who experience such a pregnancy will go on to have totally normal and healthy pregnancies afterward, but if you have suffered from multiple anembryonic pregnancies, genetic counseling might be recommended to find out the underlying cause of your losses.
- www.betterhealth.vic.gov.au/health/HealthyLiving/miscarriage?viewAsPdf=true
- www.nhs.uk/conditions/miscarriage/
- Photo courtesy of Database Center for Life Science by Wikimedia Commons: commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Ovum.png








Your thoughts on this
Loading...