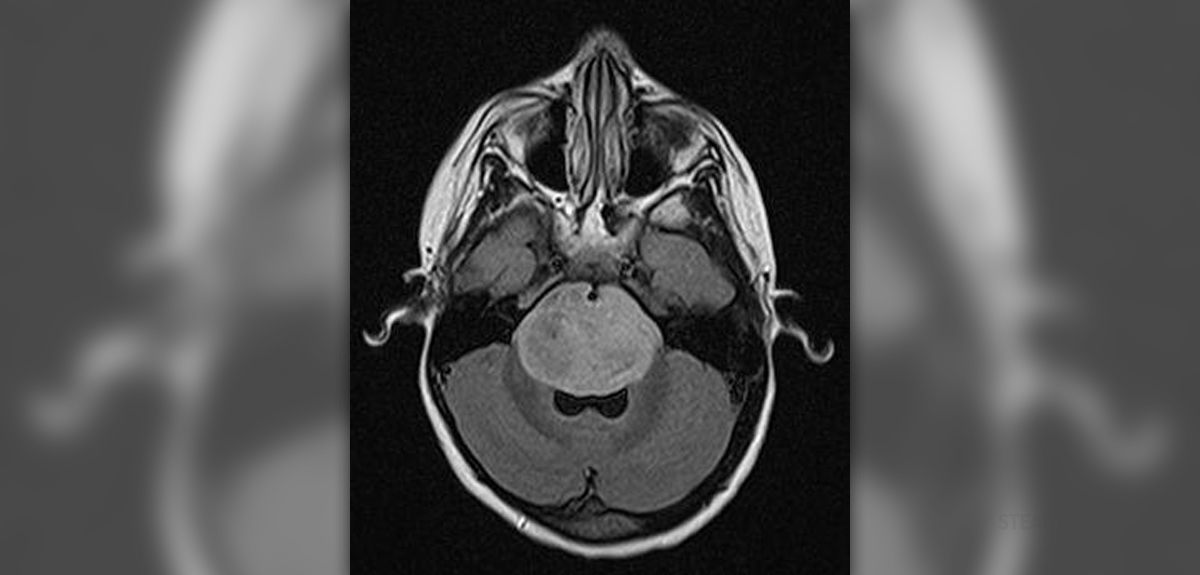
A brain tumor can be defined as an abnormal growth of tissues made of different cells that are normally found in the brain. However, such cells grow uncontrollably and form sometimes huge tumor mass which is responsible for all the symptoms and signs of the disease.
Brain Tumors Classification
Even though all brain tumors can be simply classified into benign and malignant, even benign ones act as malignant causing compression to nearby tissues and increasing the pressure inside the skull. Furthermore, benign tumors may be located in inoperable parts of the brain and because they cannot be removed, their further growth eventually leads to lethal outcome. This is the reason why the mentioned classification should be taken with restrictions. Finally, unlike primary brain tumors (those who stem from brain cells), the organ may be affected by metastases of cancers which originate from other organs in the body (e.g. the lungs, bones etc.)
Clinical Characteristics of Brain Tumors
Symptoms and signs of brain tumors basically depend on location of the tumor, as well as its size. The symptoms are, therefore, not unique. As for general symptoms of brain tumors these include headaches and mass effects.
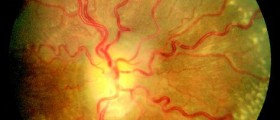
HeadachesHeadache is the most characteristic complaint of people suffering from a brain tumor. The very growth of the tumor leads to increase of intracranial pressure which eventually results in repeated or constant headaches. Such headaches are usually the worst in the morning and may gradually subside during the day. Apart from headaches patients may often vomit without warning nausea. Even after repeated vomiting they do not feel better. Headaches caused by brain tumors become more intensive with coughing, exercising and a change of position. They also do not respond to usually prescribed headache medications.Mass EffectMass effect is a consequence of growth of the tumor and an increase in intracranial pressure. The tumor grows, but the head simple cannot expand due to the fact it is made only of bones. In some cases brain tumors are small but located specifically and they block the flow of cerebrospinal fluid and induce hydrocephalus. Mass effect is seen on many parts of the brain which tend to become swollen.Some brain parts are compressed while others are displaced. The symptoms and signs of mass effect are nausea, vomiting, vision problems such as double vision or even loss of peripheral vision, headaches and a variety of mental changes. One typical sign of mass effect is swelling of an optic nerve which can be easily confirmed by an eye exam. A well experienced ophthalmologist can see papilledema by examining the fundus of the eye.
It is essential to provide with prompt treatment once symptoms and signs of mass effect occur and prevent permanent damage to different parts of the brain. This is generally achieved by surgery and elimination of excess of fluid and reduction of intracranial pressure.












Your thoughts on this
Loading...