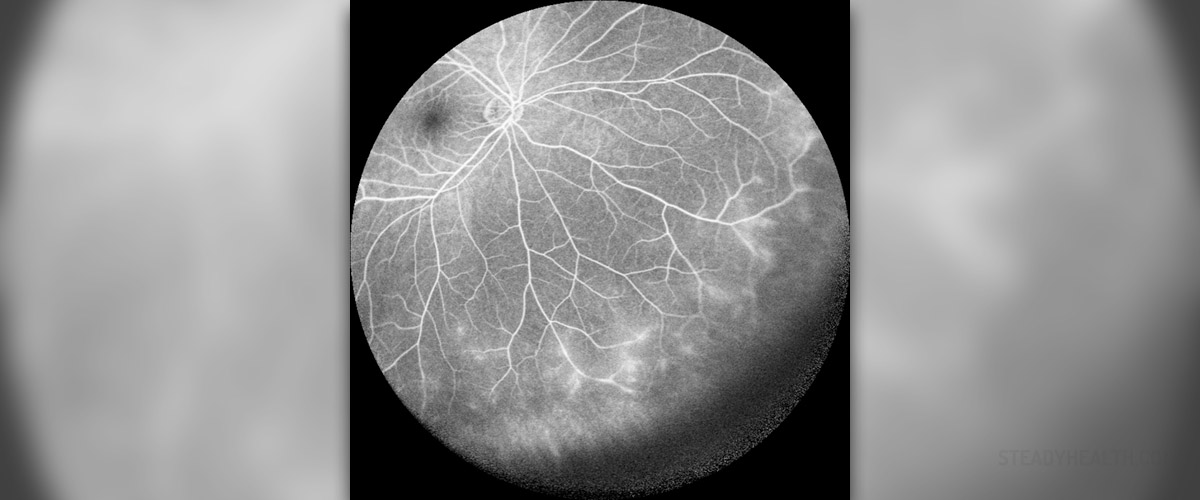
A person diagnosed with uveitis is suffering from an inflammation of the uveal tract. The uveal tract consists of the iris, ciliary body and the choroid. All of these parts of the uveal tract play an important role. Iris is responsible for the regulation of the light that enters the eye. Support of the lens and the production of aqueous humor are performed by the ciliary body. The choroid is known to provide oxygen and nourishment for the retina.
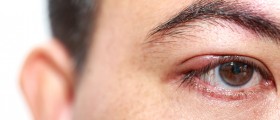
Inflammation of the eye
It is important to know that the experts have come up with a classification scheme for uveitis based upon anatomic location. Four main types of uveitis are anterior uveitis, intermediate uveitis, posterior uveitis and panuveitis. In case of anterior uveitis, the primary site of inflammation is anterior chamber and it includes iritis, iridocylitis and anterior cyclitis. Vitreous is the main site of inflammation in case of intermediate uveitis and it includes pars planitis, posterior cyclitis and hyalitis. When posterior uveitis is considered, the primary site of inflammation is the choroid and it includes focal, multifocal or diffuse choroiditis, chorioretinitis, retinochoroiditis, retinitis and neuroretinitis. The primary sites of inflammation in case of panuveitis are anterior chamber, vitreous and choroid. According to the doctors, anterior uveitis is most likely to need be in need of an emergency department. In cases when the inflammation does not go further than the iris, the medical term for the condition is iritis. In cases when the ciliary body is also involved, the condition is known as iridocyclitis. In order for the uveitis to be described better, the experts also refer to the onset, which can be sudden or insidious, duration, course and laterality. The duration of uveitis ranges from limited, which does not last for more than three months, to persistent, which lasts longer than three months. In case of course, the condition is known to be acute, recurrent or chronic. When laterality is considered, uveitis can be either unilateral or bilateral.
Treatment options for uveitis
The data in the United States claims that this condition is not that common and there are no more than 12 patients diagnosed with uveitis out of 100,000 people. The incidence is the biggest in Finland, where there are 23 cases of uveitis per 100,000 every year. The experts believe that that is the case because of the high frequency of a certain gene in people in Finland. Treatment options are not the same for every patient and they depend on various factors like the history and the signs and symptoms of the condition. There are some cases where laboratory studies are not needed. These situations are when the condition is mild, unilateral nongranulomatous uveitis caused by trauma, a certain known systemic disease or in cases where neither history nor a physical examination do not point to a certain systemic disease. In cases where laboratory workup is needed, some of the most commonly ordered tests are CBC, rapid plasma reagin, purified protein derivate, lyme titer and HLA-B27. In some cases the doctor may order a chest radiograph in order to find out whether tuberculosis or sarcoidosis are the underlying causes of the condition. In case of infectious uveitis it is important to discover the underlying cause in order to properly treat the condition. For instance, if uveitis is caused by herpes simplex virus, the doctor will focus on treating that condition and that will lead to relieving of inflammation in the eyes. If uveitis is non-infectious, corticosteroids are used most often. Corticosteroids work by disrupting the natural functioning of the immune system which releases certain chemicals that lead to the inflammation. The dose ranges depending on the severity of the condition. There are a lot of available forms of corticosteroids a person can use. The most commonly used are corticosteroid eye drops and corticosteroid injections and oral corticosteroids. Oral corticosteroids are the strongest are known to cause a lot of side effects, unlike corticosteroid injections. These side effects vary depending whether a person uses them on a short-term basis or on a long-term one. Some of the most commonly seen side effects are an increased appetite, weight gain, insomnia, fluid retention, mood changes, osteoporosis, high blood pressure, type 2 diabetes, thinning of the skin and cataracts, among others. There are some cases when none of these treatments seem to work and then immunosuppressants are used. However, they can also lead to certain side effects, some of which are severe like hair loss, skin rash, headaches, nausea, skin rash and high blood pressure.
Medication for uveitis
According to the experts, the main goal of use of medications is to reduce inflammation and pain caused by uveitis. Cycloplegics and corticosteroids are mainly used for this. Corticosteroid eye drops have been in use as a treatment option for this condition since the 1950s. Cyclopentolale 0.5-2% and Homatropine are the two most commonly used cycloplegics. When topical steroids are considered, the doctors mainly prescribe Prednisolone 1%.












Your thoughts on this
Loading...