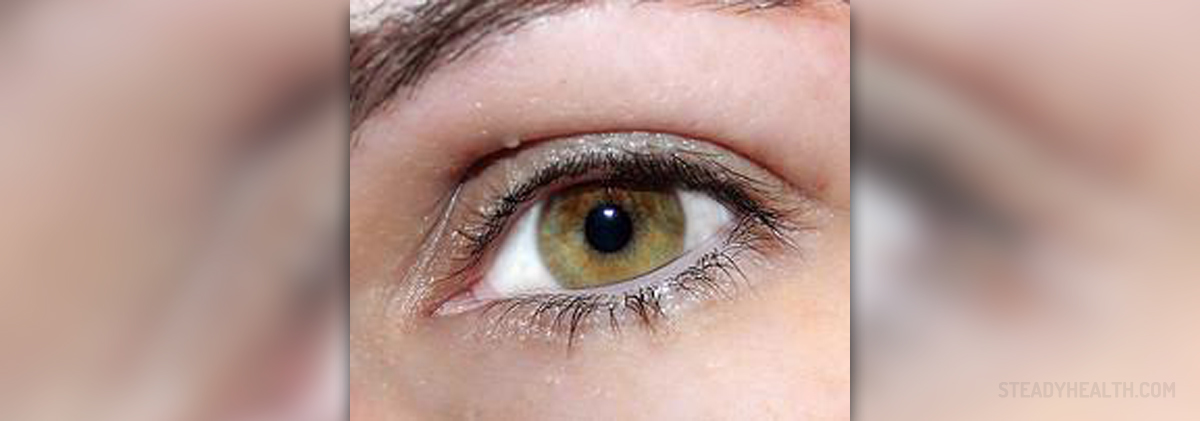
Inflammation of the middle layers of the eye (the uveal tract or the uvea of the eye) is among medical professionals known as uveitis. The uveal tract actually contains eye structures like the iris, choroid and ciliary body of the eye and it is important because it contains blood vessels essential for vision.
Uveitis Symptoms and Causes
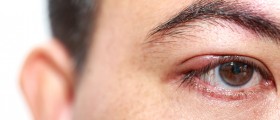
Patients suffering from uveitis usually complain about irritated and red eyes and increased sensitivity to light. Some of these patients may experience blurry vision, while others complain about floating spots before the eyes or even eye pain. Any of these symptoms may indicate uveitis, so make sure to consult your doctor or an ophthalmologist if the problem of red eye(s) does not resolve quickly in order to avoid any permanent vision problems associated with this eye disease.
Bacterial, viral, parasitic and fungal infections are the most probable causes of uveitis, but this eye condition can also be provoked by some eye injury or inflammation of any other parts of the body. Depending on the part of the uvea that gets infected, we can distinguish choroiditis, cyclitis, iritis and retinitis.Choroiditis affects the choroid and it can be caused by some infections like tuberculosis, but also by autoimmune diseases or even stress. Cyclitis affects the muscle which focuses the lens. Even though the problem usually develops suddenly it might last for several months. Iritis is inflammation of the iris, known to be related to some autoimmune diseases like rheumatoid arthritis. Retinitis is known to affect the back of the eye and usually develops due to some viral or bacterial infections of the eye (herpes, shingles, toxoplasmosis, syphilis, etc.) or because of autoimmune disorders.
How to Diagnose and Treat Uveitis?
If you happen to develop any of the symptoms mentioned before, consult the ophthalmologist and let him/her determine whether you have this inflammatory condition. Careful examination of your eyes and blood works may be needed for the purpose of proper uveitis diagnosis. In some patients, uveitis may complicate and lead to development of cataract, glaucoma, fluid within the retina, abnormal growth of blood vessels or even permanent loss of vision.
Treatment is usually delivered right after the diagnosis. Uveitis caused by infection is commonly treated with specific medications like antibiotics, antiviral agents or antifungal drugs, while eye drops with steroids might be useful for swelling in all other cases. Wear dark glasses in order to deal with light sensitivity and ask your doctor for some painkillers if your eyes hurt.













Your thoughts on this
Loading...