Cause to rib fractures
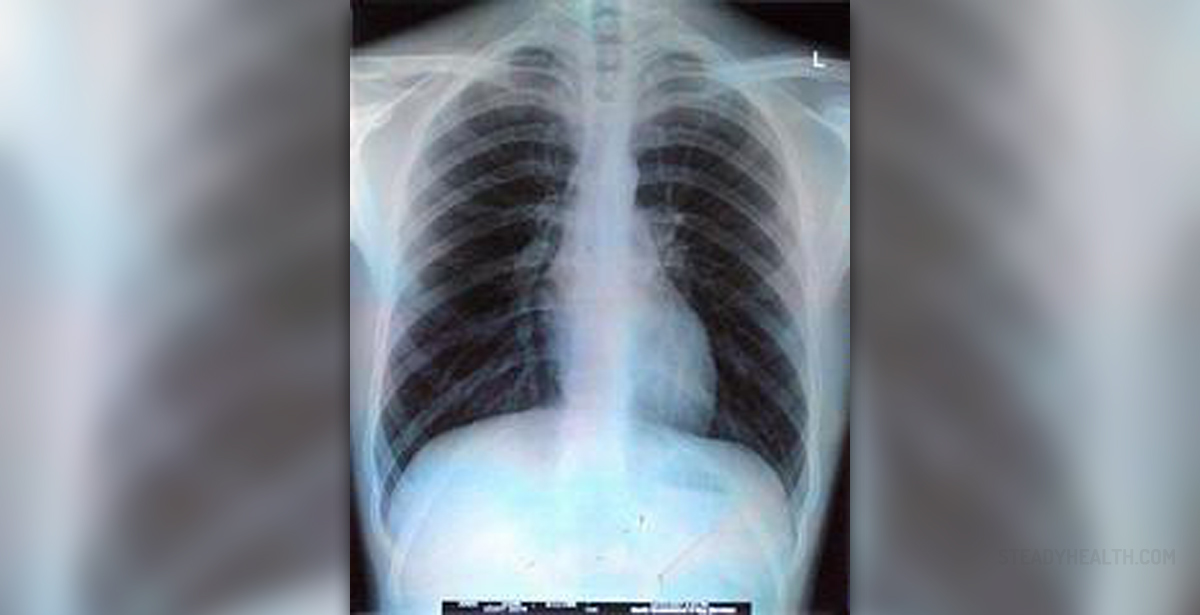
Blunt chest trauma is often accompanied by simple rib fractures. This covers over 50% of all thoracic injuries from nonpenetrating trauma. In most cases these fractures are not life threatening but may indicate a more serious internal abdomen or chest injury.Elderly usually suffer this kind of injury from falls, adults most commonly from motor vehicle accidents (MVA) while young people usually sustain rib injuries from athletic or recreational activity.
Pathophysiology
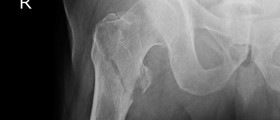
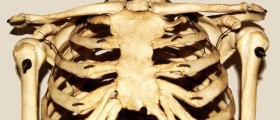
The Chest wall consists out of ribs, sternum, clavicles and scapulae. These form a hard structure that protects underlying sensitive organs. For normal respiration undamaged chest wall is a necessity.Fractured ribs can influence the breathing process in many ways. Pain caused by fractured rib cage can lead to respiratory splinting followed by pneumonia and atelectasis. Multiple rib fractures such as ‘flail chest’ can interfere with regular diaphragmatic and costovertebral muscle expansion and lead to lack of breath. Lose fractured rib fragments can cause penetration that can result in pneumothorax or hemothorax. Most commonly fractured ribs are from fourth to ninth. The most common fracture points are the impact point and at the weakest area of posterior angle. The weakest point is the subclavian artery groove in the first rib which often gets injured by a sudden forward movement of the head and back, usually occurring in motor vehicle accidents.
Rib cage injury first aid
The first thing to do is to check the airways and ensure sufficient oxygen supply.
Emergency Department Care
Emergency department is there to evaluate the trauma on the patient and bring him to a stable state. Due to the often association of rib fractures and underlying structures injury, the Emergency Department is known to consult the trauma service.First they will tend to clear the pulmonary secretion and relieve the pain. Rib fracture is the only problem and has not caused any additional damage can be managed with oral analgesics in home care. Although some studies suggest it is only a placebo, Lidocaine based patch can be used for pain relief. Patient controlled anaesthesia can reduce pain significantly with minimal influence on respiratory system. Controlled narcotics therapy may be administered in some cases to prevent respiratory depression. One way to reduce pain without influencing the respiratory functions is intercostals nerve blocks. This is a risky procedure since it includes intravascular injection and pneumothorax. To hospitalized patients, delivery of anaesthetics can be epidular or intradpleural. Another useful alternative is the patient controlled analgesia pump. Although rib binders and belts can help reduce the pain they can also cause atelectasis, hypoventilation and pneumonia. Because of this their use is not recommended.CT scan of chest and abdomen are useful for locating related injuries in patients who have been through heavy trauma.









Your thoughts on this
Loading...