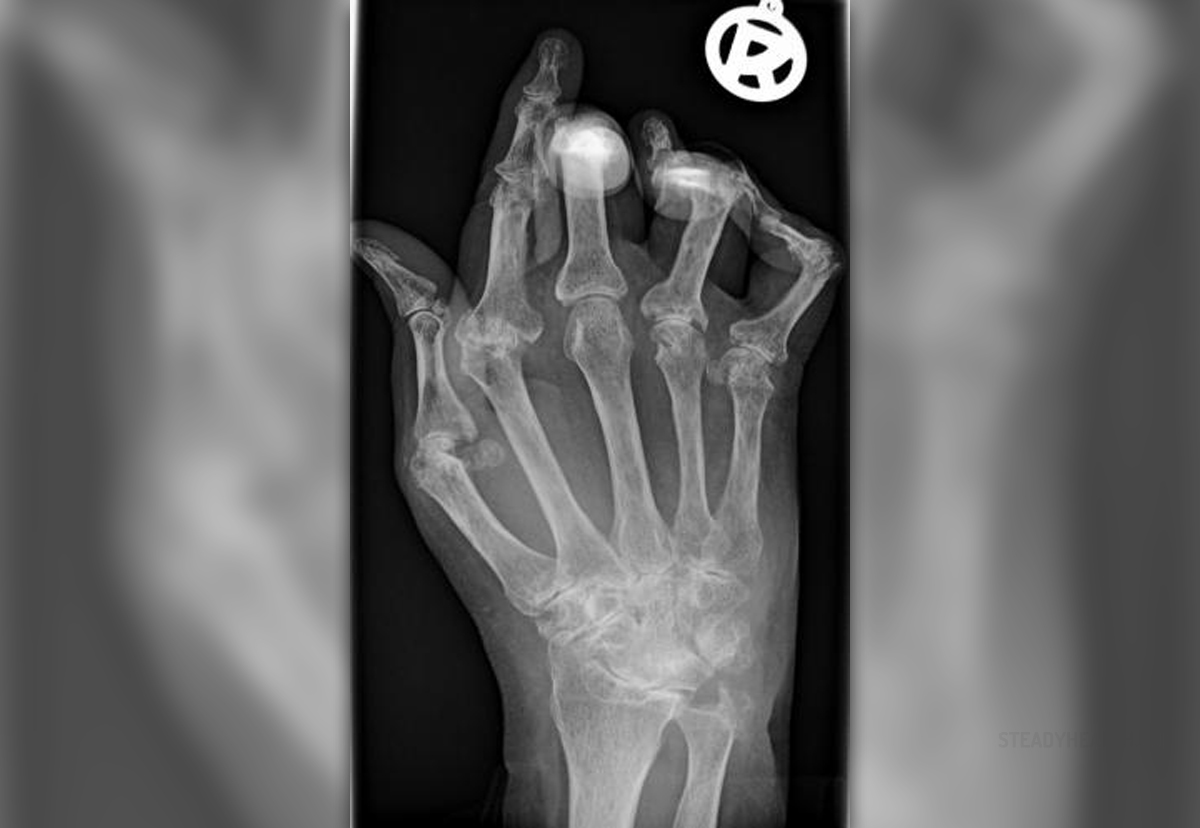
What Is Rheumatoid Arthritis?Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic inflammatory condition that affects the joints and nearby tissues but may also damage other body organs. Rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune disease that develops from an unknown cause. It develops progressively when the body’s immune system starts to mistakenly attack and destroy its own healthy tissue.
This debilitating disease usually affects the smaller joints of the hands, feet, knees, wrists and ankles on each side of the body equally.
Rheumatoid arthritis may affect people of all age groups. Women are two to three times more susceptible to rheumatoid arthritis than men.
It is believed that genes, infections and hormones can trigger rheumatoid arthritis. Specific symptoms and severity of the disease may vary greatly from patient to patient.
Rheumatoid Arthritis Symptoms
Rheumatoid arthritis initially produces non specific symptoms such as fatigue, appetite loss, low grade fever, swollen glands, weakness and weight loss. Pain in the joints develops with time. This pain appears symmetrically in the same joints on each side of the body.
Rheumatoid arthritis is accompanied with morning stiffness that may last for several hours. Joints become warm, tender and stiff but this can be relieved with motion.
Joint swelling and deformity are also present. The wrists, elbows, shoulders, fingers, hips, knees, ankles and toes are most commonly affected although the symptoms may appear in the jaw and the neck too.
Rheumatoid arthritis also causes eye burning and itching, firm bumps under the skin (nodules), chest pain and numbness, tingling or burning in hands and feet.
Treatment for Rheumatoid Arthritis
There is no cure for rheumatoid arthritis but the treatment aims to control the disease and relieve the symptoms. Treatment for RA involves medications, physical therapy, exercise, education and counseling as well as surgery if needed.
Medications
Disease modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs) are most commonly used medications in treatment of RA along with anti-inflammatory drugs, exercise and rest. Most frequently used DMARDs are methotrexate and lefluminode but since they entail serious side effects regular blood tests are required during the therapy.
Non steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) like Aspirin, ibuprofen and celecoxib are used to reduce the inflammation and relieve pain.
Corticosteroids are used for treatment of joint swelling, stiffness and inflammation but only on a short-term basis to avoid serious side effects.
Biologic agents like THF-alpha inhibitors, white blood cell inhibitors and interleukin-6 inhibitors are used in a combination with DMARDs to prevent components of the immune system from attacking the joints. They are administered intravenously or subcutaneously.
Surgery
Surgical treatment may be required in case of severely affected joints to alleviate the pain and reduce deformities. Surgical treatment involves synovectomy or removal of the lining of the joint (synovium). Total joint replacement may also be performed if necessary.
Physical Therapy
Physical therapy is used to address the inflammation and the pain of the joints as well as to preserve the joint function. Physical therapy includes heat and cold treatments, exercises to improve a range of motion, relaxation techniques and splints or orthotic devices to improve the function of the joints.











Your thoughts on this
Loading...