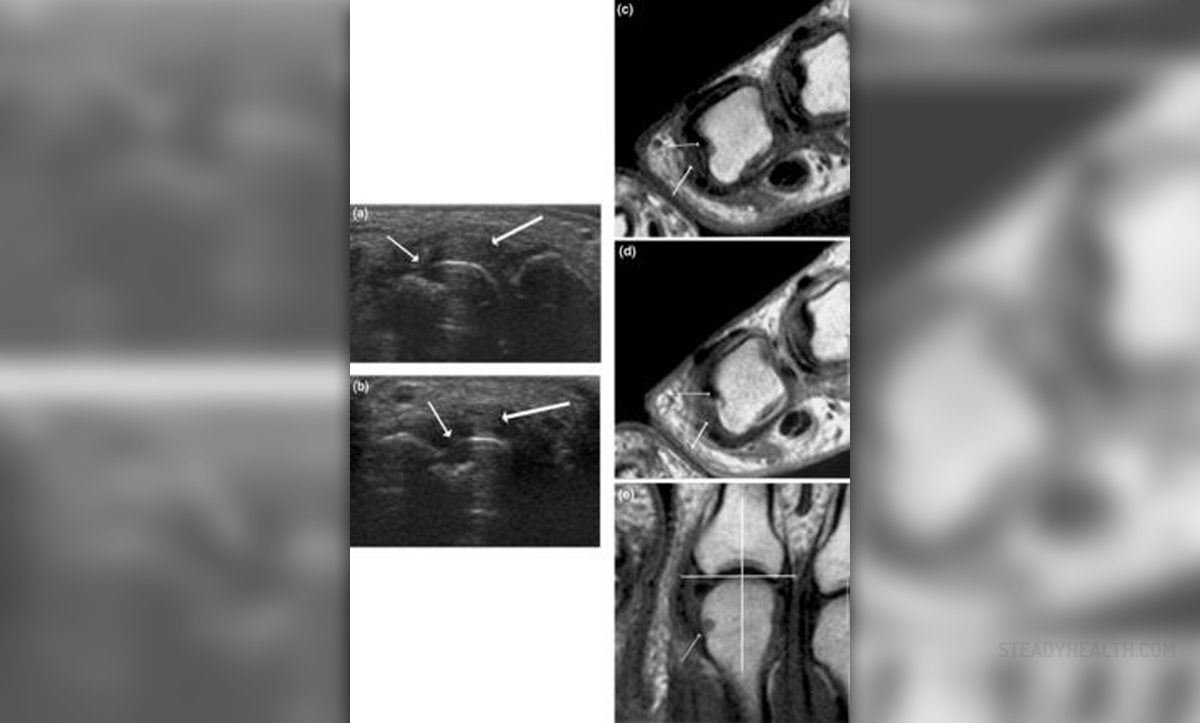
Rheumatoid arthritis is a systemic inflammatory disorder predominantly affecting joints. Damage to the synovial joints develops as a consequence of inflammation due to hyperplasia of synovial cells, over-production of synovial fluid and the development of pannus in the synovium. All the previously mentioned subsequently leads to the destruction of articular cartilage and ankylosis of the affected joints.
Apart from inflammation of different joint, the condition is blamed for inflammation of the lungs, pericardium, pleura and sclera. The condition belongs to autoimmune diseases.
Rheumatoid Arthritis Clinical Characteristics
The symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis may vary a lot and they generally depend on the affected organ/joint. They tend to become more intensive in time. Damage to the affected tissues eventually leads to different degree of disability.
Inflammation of joints is mild, moderate or severe. Pain associated with inflammation also ranges and can be sometimes tolerated while in other cases it can be only brought under control with potent pain killers. The presence of pain or deformity that generally develops in time may interfere in performing even the simplest tasks.
The affected joints are, apart from being painful, swollen and stiff. The stiffness is most intensive in the morning and then gradually subsides.
Rheumatoid Arthritis Medications
Disease modifying antirheumatic drugs represent the first line of treatment for people suffering from rheumatoid arthritis. Methotrexate is one member of this group of medications. It is prescribed alone or along with anti-inflammatory drugs. Anti-inflammatory drugs have been confirmed quite efficient in reduction of many symptoms of inflammation rheumatoid arthritis sufferers have to face with.
Patients may additionally prescribed antimalarial medications or corticosteroids. Biologic agents are more potent drugs reserved for people in whom the disease does not improve. Some biologic agents are administered subcutaneously or intravenously. There are different biologic agents prescribed for rheumatoid arthritis. Some of them are white blood cell modulators, tumor necrosis factor (TNF) inhibitors and interleukin-6 (IL-6) inhibitor.
Surgery for Rheumatoid Arthritis
Surgery is performed only if the affected joints have suffered severe deformity. Some of the available surgical procedures performed in this purpose are synovectomy (the removal of the joint lining) and total joint replacement. The shoulder, knee, hip or ankle can be surgically replaced.
Rheumatoid Arthritis Physical Therapy
Physical therapy is a powerful tool for many individuals with rheumatoid arthritis. Namely, this treatment modality comprises a specially designed exercise program prescribed by a physical therapist. The exercises keep the joint mobile and the surrounding muscles strong. Additional help is obtained from special machines that apply deep heat or electrical stimulation of the affected area. Support and proper alignment of the affected joints is achieved with splints and orthotic devices.













Your thoughts on this
Loading...