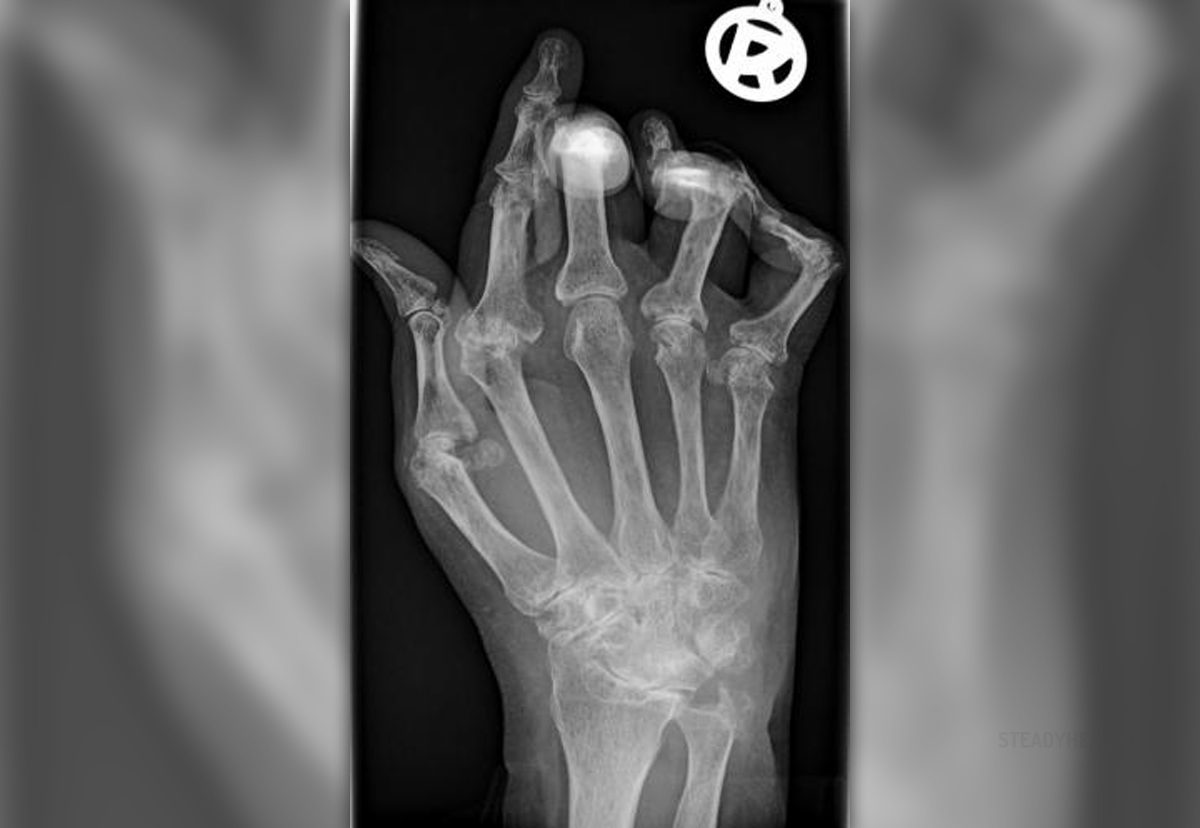
Rheumatoid arthritis is a chronic, systemic inflammatory disorder that may affect a variety of organs and tissues. However, in most cases the inflammation predominantly affects synovial joints. Once the condition develops its path is progressive and the damage to the affected tissues permanent. In a severe form of rheumatoid arthritis people suffer from serious disability.
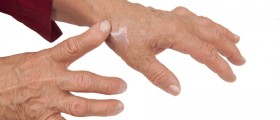
The most commonly affected joints in people suffering from rheumatoid arthritis are hands, feet, wrists and knees. Apart from joints the process of inflammation also affects nearby tissues such as muscles, tendons, ligaments and blood vessels. In certain number of patients there is an additional inflammation of the internal organs (the heart, lungs etc.).
Risk Factors for Rheumatoid Arthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis occurs in long-term smokers more than in people who do not smoke. Hence, smoking is associated with the onset of the disease. Furthermore, it is estimated that stress may also contribute to the disease. Apart from that a genetic marker HLA-DR4 is associated with increased chance of developing rheumatoid arthritis. This is why people with such feature are more prone to get the disease. There is no difference between races and all of them are susceptible to rheumatoid arthritis equally. None of the environmental factors has been confirmed to be a possible trigger for rheumatoid arthritis. This also refers to diet. And finally, the condition does not occur due to infection of any kind.
Clinical Characteristics of Rheumatoid Arthritis
People suffering from rheumatoid arthritis typically complain about joint pain, swelling and tenderness. The skin covering the affected joints is red and puffy. The joints are stiff in the morning and the stiffness may last for a long period of time. In some patients firm bumps form under the skin. They are known as rheumatoid nodules. The person feels fatigued, there is fever and weight loss.
One of the distinguishing characteristics of rheumatoid arthritis is that the disease first attacks smaller joints. Only when the condition has progressed significantly large joints become affected as well.
Treatment for Rheumatoid Arthritis
Unfortunately, there is no cure for rheumatoid arthritis. Medications reduce inflammation and relieve pain while surgery repairs damage caused by chronic inflammation.
There are many drugs prescribed in patients suffering from rheumatoid arthritis. They include NSAIDs, steroids, disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs), immunosupressants, TNF-alpha inhibitors etc. Occupation therapy is very good for such patients since it helps them find different ways to approach everyday tasks in order to reduce stress normally exerted on painful joints. These patients also benefit from a variety of assistive devices such as specially designed gripping and grabbing tools, canes etc. Surgery is performed only in case of serious damage to the affected joints. It can restore one's ability to use damaged joints again. Surgery for rheumatoid arthritis can also alleviate the pain. The most commonly performed procedures are total joint replacement, tendon repair, synovectomy (removal of the joint lining) and arthrodesis (joint fusion).













Your thoughts on this
Loading...