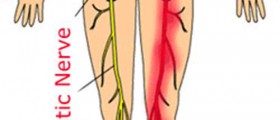
If a person suffers from a trapped nerve in the shoulder it is a medical condition commonly characterized extremely painful sensations. This medical condition may sometimes even lead to complete loss of mobility. Some people also refer to this medical condition as pinched nerve. Nevertheless, it can easily be described as a compression of the nerve between the soft tissues, cartilage, bones and muscles which surround it. Once the nerved gets pinched it easily becomes inflamed and the pinching sensations spread to other parts of the body as well. The most common causes of pinched nerve in shoulder are various physical activities of strenuous nature such as lifting of heavy objects, jogging and running. This medical condition may also be manifested as a result of bad posture in some cases. It can also be associated with some other underlying medical condition such as a formation of bone spur or a herniated disc.
Trapped Nerve in Shoulder Symptoms
All the nerves located in the shoulder are connected to different sections of the spinal cord. Certain nerves which emerge from the cervical vertebrae end up in the shoulder and they are the ones which get pinched. Each nerve is associated with a different set of accompanying symptoms once it gets pinched. When the nerve called C5 gets pinched it is commonly associated with symptoms such as sharp pain, numbness, weakness and swelling. The movement of the arms also gets somewhat restricted. If the C6 gets trapped it is usually characterized by a radiating type of pain. When the C7 gets pinched it is commonly associated with tingling and numbing sensations. The pinched C8 affects the lateral portions of the hand and it is characterized by painful sensations and numbness in fingers.
Trapped Nerve in Shoulder Treatment
In order to treat this medical condition properly, it also needs to be diagnosed properly. A physical examination of the shoulder and a revision of all physical activities of the patient are necessary. The doctor also needs to be fully informed about all the symptoms which accompany the condition. Some serious cases may also require blood tests and MRI scans as well. The patient needs to provide the affected area and the tissues which surround it with as much rest as possible. Hot and cold compresses are also very helpful in most cases. Prescription relaxers and pain killers may also be used. Some cases may require administration of cortisone injections.










Your thoughts on this
Loading...