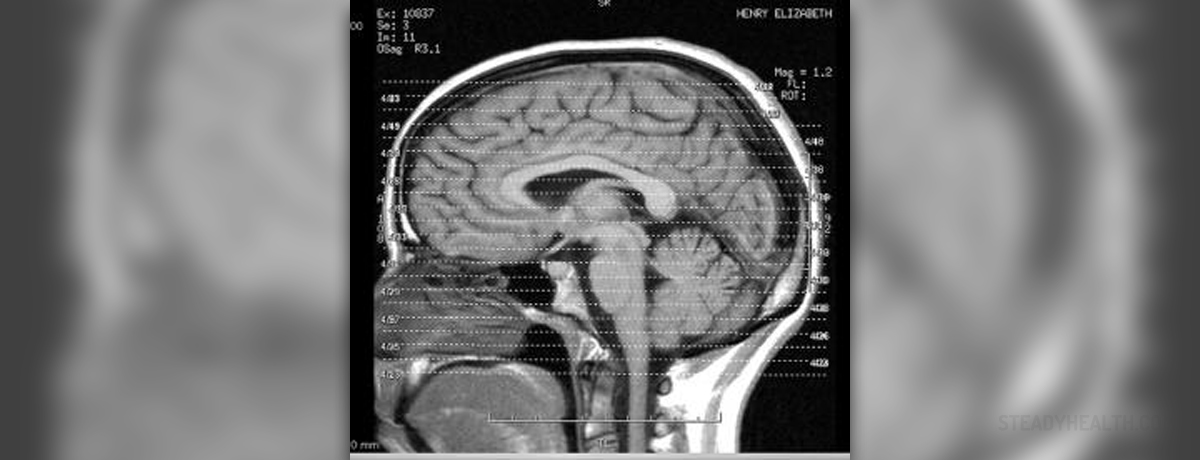
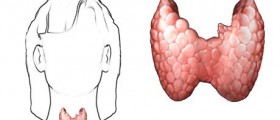
Pituitary gland is an endocrine gland located at the base of the brain. This gland is shaped like a pea, and weighs somewhere around 0.5 grams. The gland is, actually, a protrusion of the bottom part of the hypothalamus, a portion of a brain which connects the nervous system and endocrine system, using the pituitary gland. Another name for this gland is hypophysis. It is placed in a bone cavity and covered by a dural fold, which helps to keep it in the cerebrospinal fluid. Pituitary gland is very important for human body since it secretes no less than nine different hormones.
Functions of the pituitary gland
Human brain controls many different processes using the pituitary gland. This gland is especially important for normal growth and excessive amounts of one of the pituitary growth hormones may even lead to gigantism and acromegaly. Gigantism is characterized by excessive growth and height significantly above average, while acromegaly results in severe disfigurement, swelling of the tissue of the organs, pronounced brow and lower jaw protrusion, hyperpigmentation, etc.
This gland also regulates the blood pressure, maintains the proper homeostasis by regulating water and osmolarity in the body controls the reabsorption of water by the kidneys, and regulates bodily temperature.
It also produces the thyroid-stimulating hormone, which controls the thyroid gland. Hormones produced by the thyroid gland regulate the rate of metabolism and the way the human body uses calcium.
This gland is especially important during pregnancy and childbirth, since it stimulates the contractions of uterine, which is the crucial aspect of delivery. Even after the delivery, the gland remains important for breast milk production. Pituitary gland is also responsible for normal functioning of sex organs in both sexes.
Hormones of the pituitary gland
Pituitary gland is divided into three sections: the anterior lobe, the intermediate lobe, and the posterior lobe. Most of the hormones are produced in the anterior lobe. These include prolactin, which stimulates the milk production in women; growth hormone; ACTH (adrenocorticotropic hormone), which stimulates the adrenal glands; TSH (thyroid-stimulating hormone), which stimulates the thyroid gland; FSH (follicle-stimulating hormone) and LH (luteinizing hormone), which stimulate the ovaries and testicles.
Intermediate lobe of the pituitary gland produces a melanocyte-stimulating hormone, which controls the skin pigmentation.
The posterior lobe of the pituitary gland produces ADH (antidiuretic hormone), used to stimulate the kidneys to absorb more water into the blood. This lobe also produces oxytocin, which helps during the delivery by stimulating the uterus to contractions and controls the milk production in lactating women.







-In-Adults_f_280x120.jpg)


-In-Infants-And-Older-Children_f_280x120.jpg)
Your thoughts on this
Loading...