Abnormal growth in the pituitary gland is pituitary tumor. In many cases the tumor that forms in the pituitary gland is benign or non-cancerous and it is termed as pituitary adenoma. Pituitary adenoma does not spread outside the skull and remains confined to the gland.
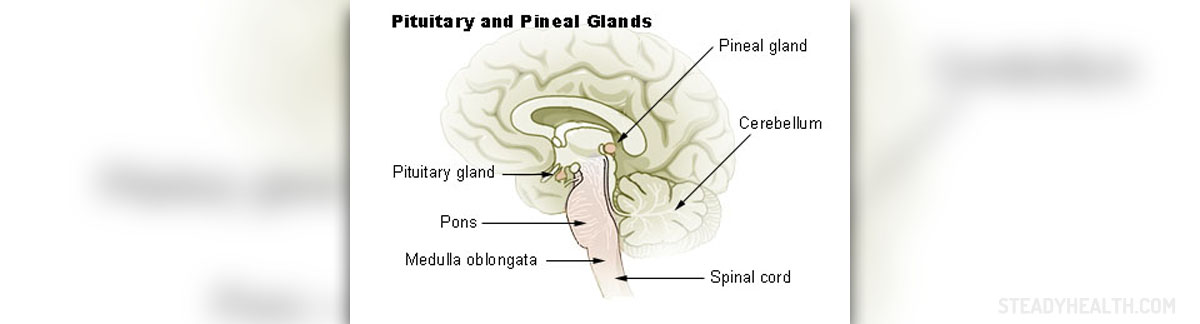
What is Pituitary Gland?The pituitary gland is a small, pea-sized organ located at the base of the brain. It is also known as hypophysis and “master” gland because it regulates functioning of the endocrine system. The pituitary gland produces many hormones and stimulates other glands of the endocrine system to secrete hormones. The pituitary gland is responsible for different body processes such as growth, metabolism, temperature regulation and reproduction. Hormones produced and released by the pituitary gland are: growth hormone (GH), prolactin, adrenocorticotropin (ACTH), antidiretic hormone (ADH), thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH), lutenizing hormone (LH) and follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH). All in all, normal functioning of the pituitary gland is essential to human well-being. However, this gland can be affected by different disorders but the most frequent disorder of the pituitary gland is pituitary tumor or adenoma. This condition interferes with the production and release of hormones.
Pituitary Adenoma
Pituitary adenoma is a benign, non metastatic growth. It is a common condition that most frequently affects young and middle-aged adults. In many people the condition is never diagnosed because it usually doesn't have any symptoms. Exact cause of pituitary gland tumor is still unexplained but experts believe that acombination of hereditary and environmental factors are responsible for the formation of the tumor. There are two types of pituitary adenomas, namely secretory and non-secretory. They can result in hypersecretion, when too much pituitary hormones are released into the body and hyposecretion in which too little hormones are secreted. Both hypersecretion and hyposecretion lead to hormonal imbalance. Tumor mass effect refers to any pituitary tumor (secretory or non-secretory) that becomes large enough to press against and damage nearby pituitary tissue.
Pituitary Adenoma Symptoms
The symptoms depend on type of pituitary adenoma and hormone that is affected. Prolactin secreting tumor can cause symptoms such as: infertility, irregular menstruation, amenorrhea (absence of menstruation), decreased sex drive, nipple discharge (galactorrhea), osteoporosis, vaginal dryness, excess hair growth and impotence in males. ACTH secreting tumor can cause Cushing’s disease associated with symptoms like: hypertension, diabetes, flushed face, skin ulcers, mood swings, thin skin and decreased fertility in men. Growth hormone secreting tumor results in acromegaly followed by symptoms such as: gigantism, soft tissue enlargement, spreading teeth, Bell’s palsy, excessive perspiration, oily skin, impotence and bone and joint pain. Tumor mass effect causes headache, lethargy, nasal discharge, nausea, vomiting, visual problems, dizziness, seizures and temperature intolerance.
Diagnosis and Treatment of Pituitary AdenomaPituitary adenoma is commonly diagnosed with imaging tests such as CT or MRI scans. Endocrine function tests and visual field testing are also conducted to confirm diagnosis. Pituitary adenoma can be treated surgically as well as with radiation and medication to shrink the size of the tumor.







-In-Infants-And-Older-Children_f_280x120.jpg)




Your thoughts on this
Loading...